Figure 5. Dependence of the relaxation process  on the magnitude and duration of a stimulus.
on the magnitude and duration of a stimulus.
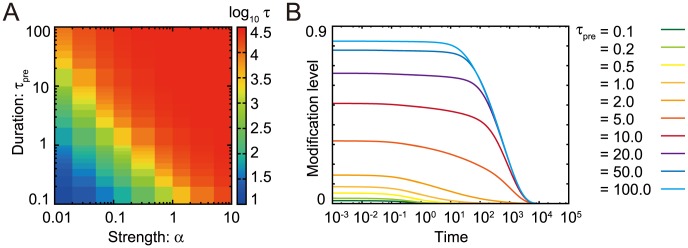
(A) The relaxation time after exposure to the stimulus with various magnitudes and durations is plotted as a color map. The initial condition is given as 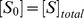 and
and 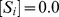 for
for  , and the input is given as
, and the input is given as 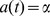 for
for 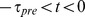 and
and 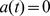 for
for 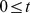 . When the magnitude (
. When the magnitude ( ) and duration of the stimulus (
) and duration of the stimulus (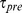 ) increase,
) increase,  increases continuously over an order of magnitude. The catalyst concentration is set at
increases continuously over an order of magnitude. The catalyst concentration is set at 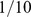 of the substrate concentration. (B) Dependence of the relaxation process on the duration of stimulus exposure. The duration of stimulus exposure is changed while the magnitude is fixed at
of the substrate concentration. (B) Dependence of the relaxation process on the duration of stimulus exposure. The duration of stimulus exposure is changed while the magnitude is fixed at 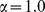 . Here, the relaxation time increases nearly exponentially with the increase in duration for the some extent small
. Here, the relaxation time increases nearly exponentially with the increase in duration for the some extent small 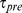 . When
. When 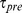 is sufficiently long, the modification is maintained for a long time.
is sufficiently long, the modification is maintained for a long time.
