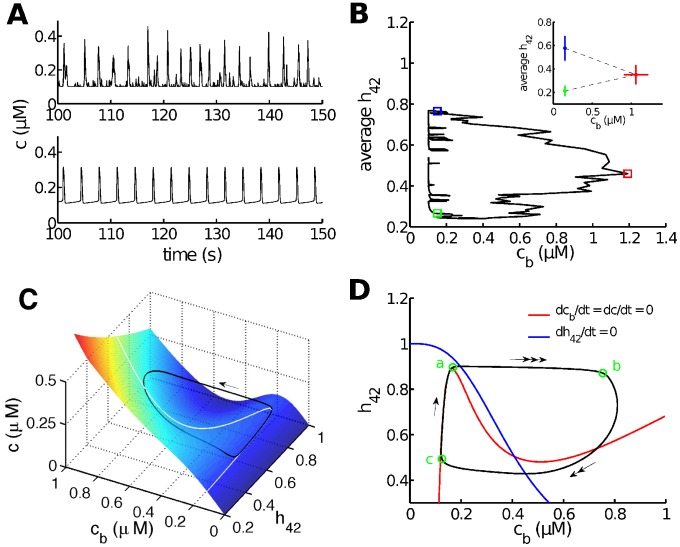
Figure 5. Stochastic and deterministic simulations exhibit similar dynamic properties.
A: simulated stochastic (upper panel) or deterministic (lower panel) 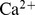 oscillations at
oscillations at 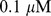
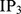 . B: a typical stochastic solution projected on the
. B: a typical stochastic solution projected on the 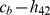 plane. The average
plane. The average 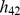 represents the average value of
represents the average value of 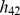 over the 20
over the 20 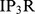 . Statistics (
. Statistics (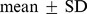 ) of the initiation point (blue square), the peak (red square) and termination point (green square) are shown in the inset. 116 samples are obtained by applying a low threshold of
) of the initiation point (blue square), the peak (red square) and termination point (green square) are shown in the inset. 116 samples are obtained by applying a low threshold of 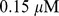 and a high threshold of
and a high threshold of 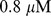 to
to 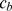 . C: a typical periodic solution of the deterministic model (black curve), plotted in the
. C: a typical periodic solution of the deterministic model (black curve), plotted in the 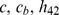 phase space. The arrow indicates the direction of movement.
phase space. The arrow indicates the direction of movement. 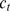 is the slowest variable so that its variation during an oscillation is very small. This allows to treat
is the slowest variable so that its variation during an oscillation is very small. This allows to treat 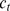 as a constant (
as a constant (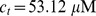 in this case) and study the dynamics of the model in the
in this case) and study the dynamics of the model in the 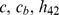 phase space. The color surface is the surface where
phase space. The color surface is the surface where 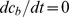 (called the critical manifold). The white N-shaped curve is the intersection of the critical manifold and the surface
(called the critical manifold). The white N-shaped curve is the intersection of the critical manifold and the surface 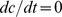 . D: projection of the periodic solution to the
. D: projection of the periodic solution to the 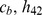 plane. The red N-shaped curve is the projection to the
plane. The red N-shaped curve is the projection to the 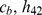 plane of the white curve shown in C. The evolution of the deterministic solution exhibits three different time scales separated by green circles (labelled by a, b and c) and indicated by arrows (triple arrow: fastest; double arrow: intermediate; single arrow: slowest).
plane of the white curve shown in C. The evolution of the deterministic solution exhibits three different time scales separated by green circles (labelled by a, b and c) and indicated by arrows (triple arrow: fastest; double arrow: intermediate; single arrow: slowest).