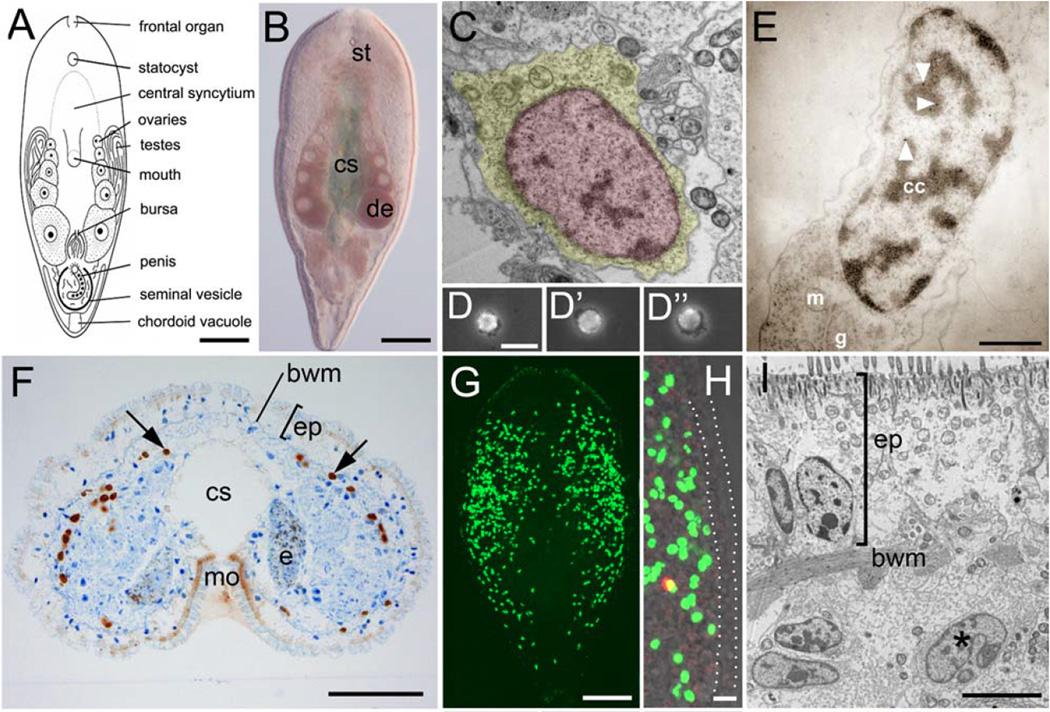
Figure 6.
“The stem cell system of Isodiametra pulchra (A,B). Morphology (C–E) and distribution (F–I) of neoblasts. (A) Schematic drawing. (B) Differential interference contrast image. (C) Typical neoblast with nucleus (red) and thin rim of cytoplasm (yellow). (D-D”) Macerated BrdU labeled cells show typical neoblast-like morphology (E) BrdU labeled neoblast, as shown by immunogold staining after a 30 min BrdU pulse; arrowheads point to gold particles. (F) Histological cross section; brown spots are BrdU labeled S-phase cells. (G,H) Confocal projection overview (G) and detail of lateral body margin (H) after 30 min BrdU pulse; the red spot in (H) is a mitotic figure. Note that S-phase cells [green fluorescence] were lacking in the epidermis (between dotted lines). (I) Electron microscopic image of a posterior-lateral body margin.” “bwm, body wall musculature; cc, condensed chromatin; cs, central syncytium; e, egg; de, developing eggs; ep, epidermis; g, Golgi; m, mitochondria; mo, mouth opening; st, statocyst. Scale bars (A,B,G) 100 µm; (C,E) 1 µm; (D,H) 10 µm; (F) 25 µm; (I) 5 µm.” Figure and legend are reprinted (with some terms excluded from the quoted term list) from Fig. 1A–I of the open-access report of De Mulder et al. (2009a).