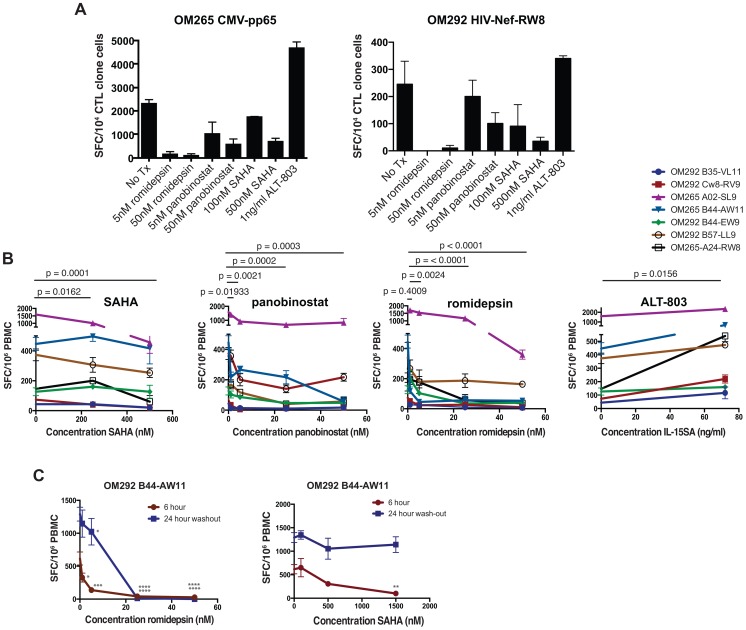
Figure 4. HDAC inhibitors impair IFN-γ production from antigen-stimulated CD8+ T-cells.
A, B. PBMC or CTL clones from chronically HIV-infected ARV-treated subjects (OM265 and OM292) were cultured for 2 hours with the indicated drugs and then plated for IFN-γ ELISPOT assays with 12 hour peptide stimulation periods. A. Treated CTL clones were stimulated with overlapping 15mer peptides spanning the CMV-pp65 protein (left panel) or the MHC-I-A24 restricted HIV-Nef peptide ‘RW8’ (right panel). Each treatment condition was tested in duplicate. Shown are mean SFC/104 CTL clone cells for each condition with error bars representing SEM. B. Experiments analogous to those depicted in A were performed for 8 different optimal HIV CD8+ T-cell epitopes (5 for OM292 and 1 for OM265). Shown are summary data for all 8 responses depicting the mean SFC/106 PBMC (of triplicate wells) under different treatment conditions. For SAHA, panobinostat, and romidepsin conditions statistical significance for each drug was evaluated using two-way ANOVA tests, and p values were calculated using Dunnett's multiple comparison test to account for the use of three different drug concentrations. For IL-15SA p values were calculated using the Wilcoxon matched pair test. C. PBMC from subjects OM265 and OM292 were treated with SAHA or romidepsin at the indicated concentrations for 2 hours and then either: stimulated with peptides for 6 a hour ELISPOT assay, or washed, cultured for 24 hours in the absence of drugs, and stimulated with peptides for a 12 hours ELISPOT assay. P values were calculated by two-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison test (comparing to the no drug control) * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001.