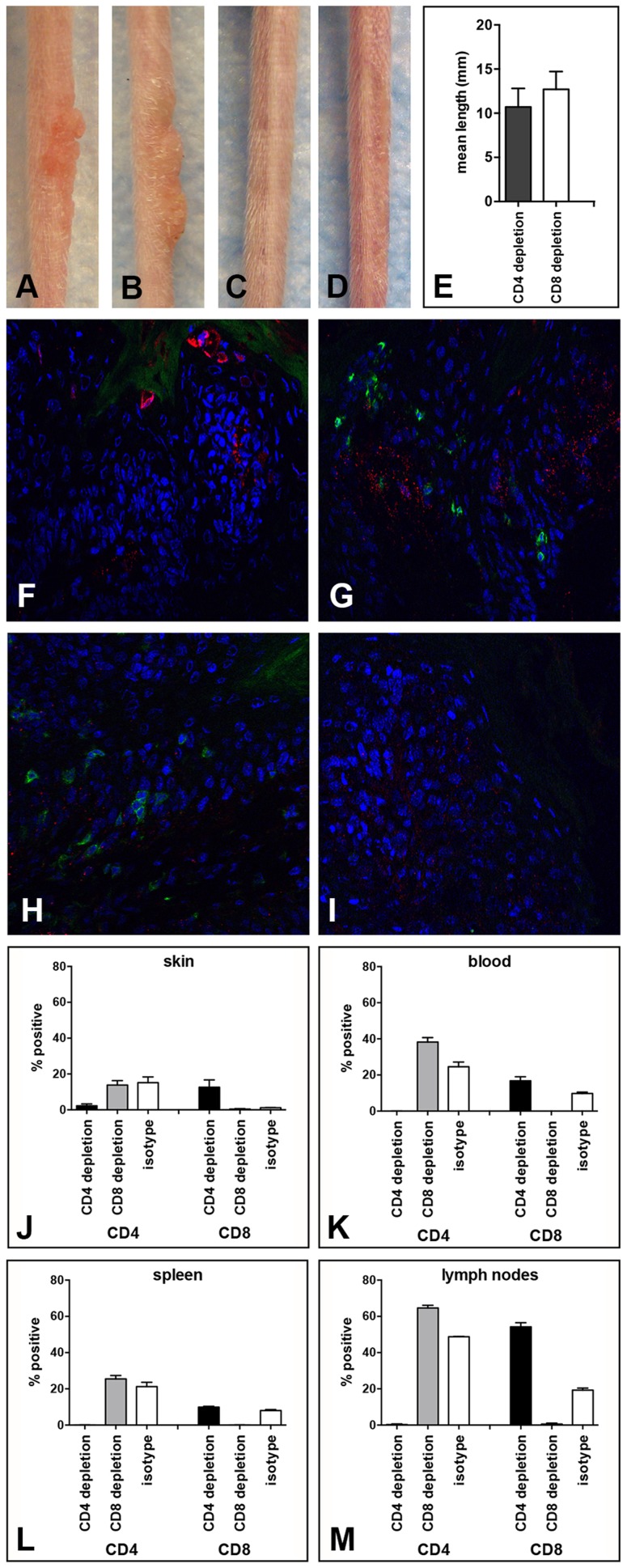
Figure 4. Papilloma formation can be observed in CD4- or CD8-depleted Cr:ORL SENCAR mice.
Antibody-mediated depletion of (A) CD4+ T cells allows papilloma formation in Cr:ORL SENCAR mice after 7 weeks of immunodepletion (6 weeks post-infection). (B) Similarly, papilloma formation was observed in CD8-depleted littermates at the same time point. (C) Isotype-depleted and (D) MusPV1-infected controls did not develop papillomas. All mice were infected with 5.1×109 MusPV1 virions. (E) Comparison of tail lesions of CD4- and CD8-depleted animals at this time point showed comparable mean lesion lengths, in mm, in these animals. Data represent the mean ± SEM of nine mice/group from a representative experiment. Immunofluorescent staining of skin tissues from (F,G) CD4-depleted or (H, I) CD8-depleted mice demonstrated abundant expression of MusPV1 L1 proteins (red, detected with an Alexa Fluor 594-labeled secondary antibody) in these tissues. Co-stainings using an Alexa Fluor 488-labeled anti-CD4 (F, H) or an Alexa Fluor 488-labeled anti-CD8 (G, I) antibody (green) confirmed the absence of the targeted T cell subpopulation in the tissues. There was no loss in the infiltration by the non-depleted subset. Quantification of CD4+ (left side) and CD8+ (right side) T lymphocytes in (J) skin, (K) blood, (L) spleen and (M) draining lymph nodes of CD4-, CD8- and isotype-depleted MusPV1-infected Cr:ORL SENCAR mice by flow cytometry analyses was performed after 5 weeks of immunodepletion (corresponding to 4 weeks post-infection) and demonstrated the efficient and specific depletion of the targeted subpopulation in each compartment.