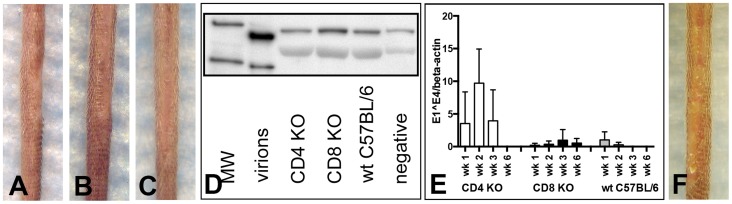
Figure 6. CD4- and CD8-deficient C57BL/6 mice differ in MusPV1 gene transcription early after infecton.
(A) CD4-deficient (n = 5), (B) CD8-deficient (n = 5), and (C) wild-type C57BL/6 mice did not develop papillomas within 3 months after infection with 9.4×1010 MusPV1 virions. (D) Western Blot analysis for the presence of MusPV1 L1 protein in crude skin tissue extracts taken from MusPV1-infected CD4-deficient, CD8-deficient, and wild-type C57BL/6 mice as well as from mock-infected controls verified the lack of MusPV1 L1 protein in these tissues. One representative per group is shown. The molecular weight marker (MW) is depicted on the left side and 60 kD and 50 kD markers are visible; purified MusPV1 virions served as controls. (E) High levels of MusPV1 E1∧E4 spliced transcripts relative to endogenous beta-actin were determined in skin tissues from CD4-deficient C57BL/6 mice during the first 3 weeks and became undetectable within 6 weeks after infection. Very low, but detectable levels of MusPV1 E1∧E4 transcripts per beta-actin were observed in CD8-deficient C57BL/6 mice. MusPV1 E1∧E4 levels were very low up to 2 weeks post-infection in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and became undetectable after week 3 post-infection. Data represent the mean ± SD of five mice/group from a representative experiment. (F) CD1d-deficient C57BL/6 mice (n = 5) did not develop papillomas within 3.5 months after infection with 6.8×1010 MusPV1 virions.