Abstract
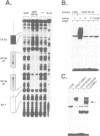
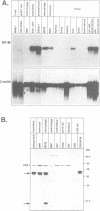
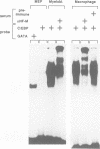
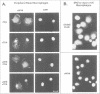
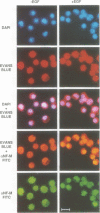
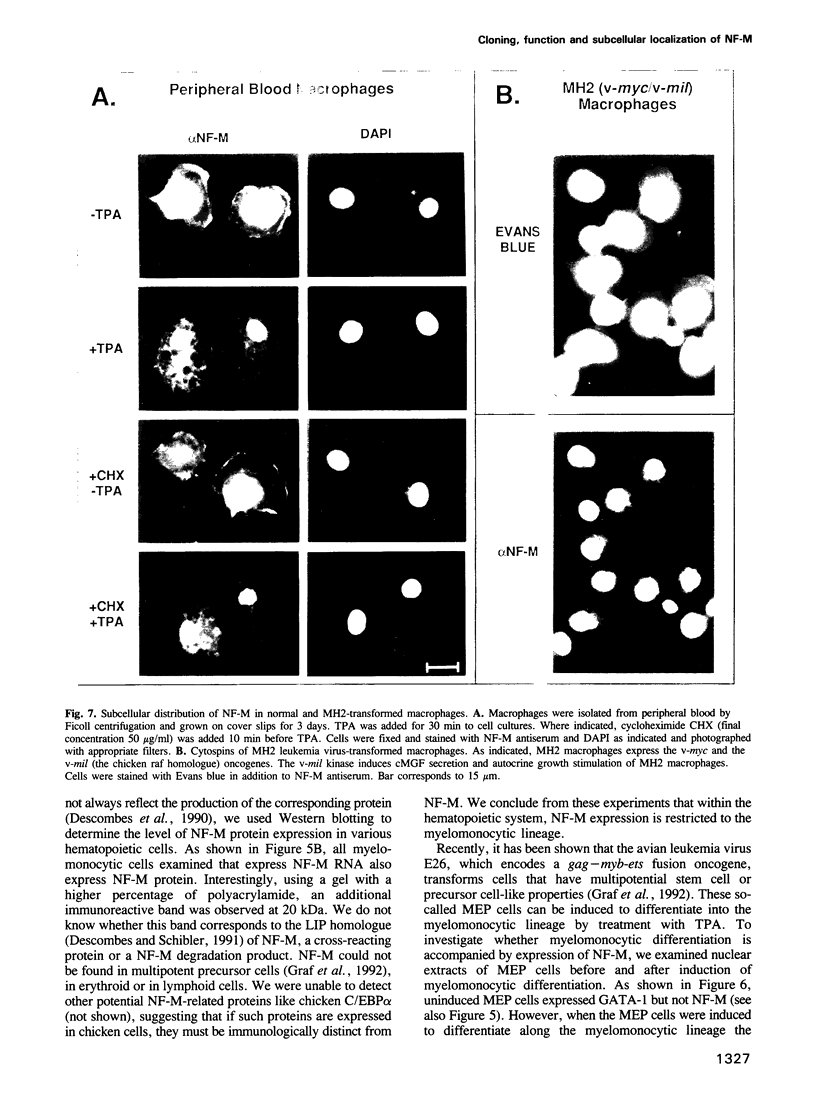
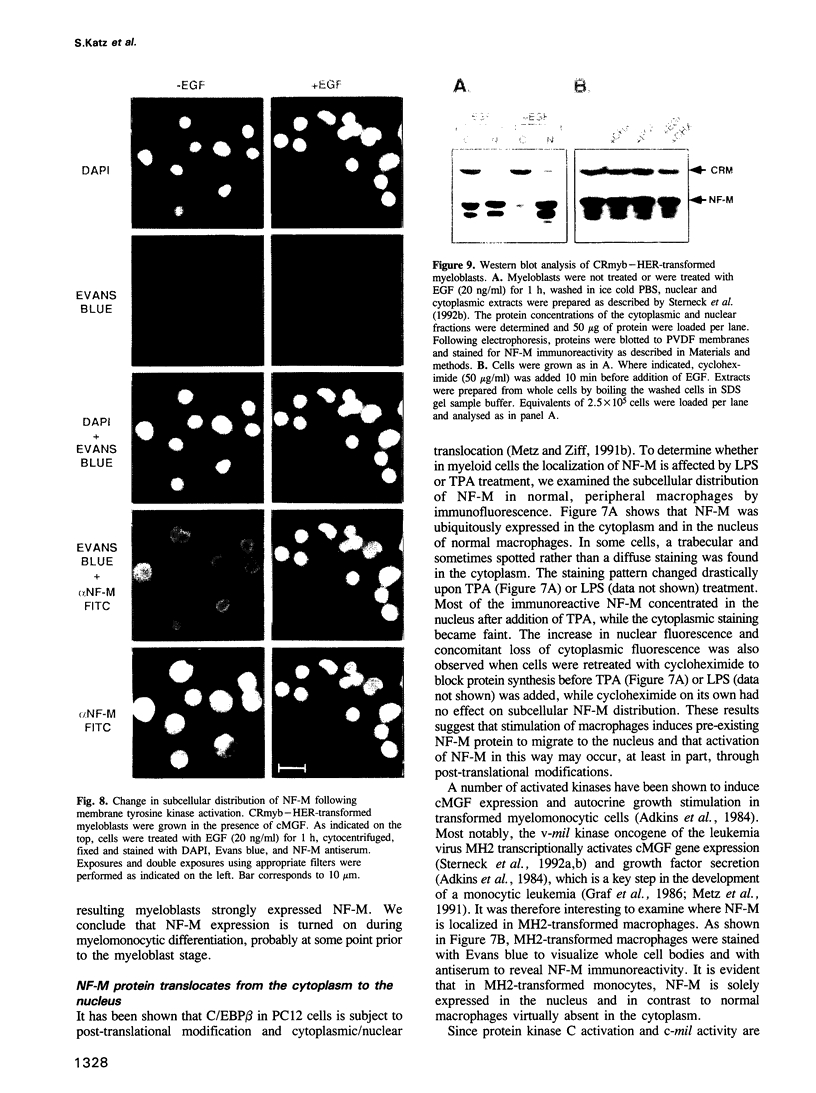
Retroviral oncogenes encode nuclear regulators of gene expression or signal transduction molecules, such as protein kinases, which stimulate the activity of cellular transcription factors. Here we describe the cloning of NF-M, a myeloid-specific transcription factor related to C/EBP beta, which is a target of activated protein kinases. NF-M stimulates the expression of the gene encoding cMGF, a myeloid cell-specific growth factor, creating an autocrine growth loop crucial to oncogene transformation of myeloid cells. The NF-M protein bound directly to the cMGF gene promoter and activated its transcription, even in erythroid cells where the promoter is usually inactive. In addition, a truncated, dominant-negative form of NF-M inhibited cMGF expression in macrophages, indicating that NF-M is required for the normal activation of the gene. When multipotent hematopoietic progenitor cells were stimulated to differentiate, NF-M expression was induced at a very early stage, suggesting that the transcription factor plays a role in lineage commitment. The stimulation of transformed myelomonocytic cells or of normal peripheral blood macrophages with kinases or LPS or TPA respectively, led to the rapid redistribution of NF-M protein from the cell bodies to the nucleus, consistent with the notion that NF-M was directly affected by such treatments. Our data indicate that NF-M plays a key role in myelomonocytic differentiation, in signal transduction during macrophage activation and in the development of myelogenous leukemia.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adkins B., Leutz A., Graf T. Autocrine growth induced by src-related oncogenes in transformed chicken myeloid cells. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Doederlein G., Freudenstein C., Graf T. Erythroblast cell lines transformed by a temperature-sensitive mutant of avian erythroblastosis virus: a model system to study erythroid differentiation in vitro. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1982;1:195–207. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Leutz A., Kahn P., Graf T. Ts mutants of E26 leukemia virus allow transformed myeloblasts, but not erythroblasts or fibroblasts, to differentiate at the nonpermissive temperature. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90465-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Müller H., Grieser S., Doederlein G., Graf T. Hematopoietic cells transformed in vitro by REVT avian reticuloendotheliosis virus express characteristics of very immature lymphoid cells. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):295–309. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., von Kirchbach A., Döderlein G., Conscience J. F., Graf T. Chicken hematopoietic cells transformed by seven strains of defective avian leukemia viruses display three distinct phenotypes of differentiation. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):375–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. J., Chen T. T., Lei H. Y., Chen D. S., Lee S. C. Molecular cloning of a transcription factor, AGP/EBP, that belongs to members of the C/EBP family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6642–6653. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll J., Righi M., Taisne C., Dissous C., Gegonne A., Stehelin D. Molecular cloning of the avian acute transforming retrovirus MH2 reveals a novel cell-derived sequence (v-mil) in addition to the myc oncogene. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2189–2194. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01722.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Schibler U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The Drosophila developmental gene, engrailed, encodes a sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):630–635. doi: 10.1038/318630a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., McNagny K., Brady G., Frampton J. Chicken "erythroid" cells transformed by the Gag-Myb-Ets-encoding E26 leukemia virus are multipotent. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):201–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90096-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Royer-Pokora B., Meyer-Glauner W., Beug H. Tumor specificity of acute avian leukemia viruses reflected by their transformation target cell specificity in vitro. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1977;164(1-3):139–153. doi: 10.1007/BF02121310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., von Weizsaecker F., Grieser S., Coll J., Stehelin D., Patschinsky T., Bister K., Bechade C., Calothy G., Leutz A. v-mil induces autocrine growth and enhanced tumorigenicity in v-myc-transformed avian macrophages. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas J. G., Ströbel M., Leutz A., Wendelgass P., Müller C., Sterneck E., Riethmüller G., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W. Constitutive monocyte-restricted activity of NF-M, a nuclear factor that binds to a C/EBP motif. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb P., McKnight S. L. Diversity and specificity in transcriptional regulation: the benefits of heterotypic dimerization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90167-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leutz A., Beug H., Graf T. Purification and characterization of cMGF, a novel chicken myelomonocytic growth factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3191–3197. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leutz A., Damm K., Sterneck E., Kowenz E., Ness S., Frank R., Gausepohl H., Pan Y. C., Smart J., Hayman M. Molecular cloning of the chicken myelomonocytic growth factor (cMGF) reveals relationship to interleukin 6 and granulocyte colony stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):175–181. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévesque J. P., Sansilvestri P., Hatzfeld A., Hatzfeld J. DNA transfection in COS cells: a low-cost serum-free method compared to lipofection. Biotechniques. 1991 Sep;11(3):313-4, 316-8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz R., Ziff E. The helix-loop-helix protein rE12 and the C/EBP-related factor rNFIL-6 bind to neighboring sites within the c-fos serum response element. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2165–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz R., Ziff E. cAMP stimulates the C/EBP-related transcription factor rNFIL-6 to trans-locate to the nucleus and induce c-fos transcription. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1754–1766. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz T., Graf T., Leutz A. Activation of cMGF expression is a critical step in avian myeloid leukemogenesis. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):837–844. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08016.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. An LFA-3 cDNA encodes a phospholipid-linked membrane protein homologous to its receptor CD2. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):840–842. doi: 10.1038/329840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterneck E., Blattner C., Graf T., Leutz A. Structure of the chicken myelomonocytic growth factor gene and specific activation of its promoter in avian myelomonocytic cells by protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1728–1735. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterneck E., Müller C., Katz S., Leutz A. Autocrine growth induced by kinase type oncogenes in myeloid cells requires AP-1 and NF-M, a myeloid specific, C/EBP-like factor. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):115–126. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Cantwell C. A., Johnson P. F. A family of C/EBP-related proteins capable of forming covalently linked leucine zipper dimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1553–1567. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]