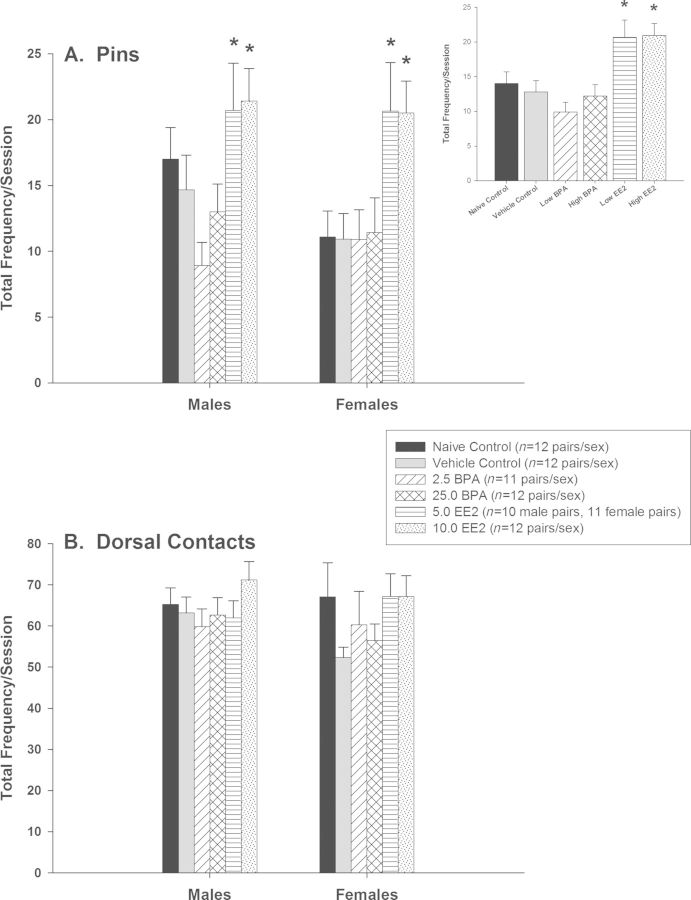
FIG. 3.
Play behavior of male and female offspring (mean ± SE). (A) Frequency of pins by treatment group and sex. A significant effect of treatment indicated that the 5.0 and 10.0 EE2 groups engaged in more pinning behavior than the vehicle control group. The treatment × sex interaction was not statistically significant (p = 0.691). Inset shows the effect by treatment group. (B) Frequency of dorsal contacts by treatment group and sex. There were no significant treatment group or sex differences on this play behavior endpoint.