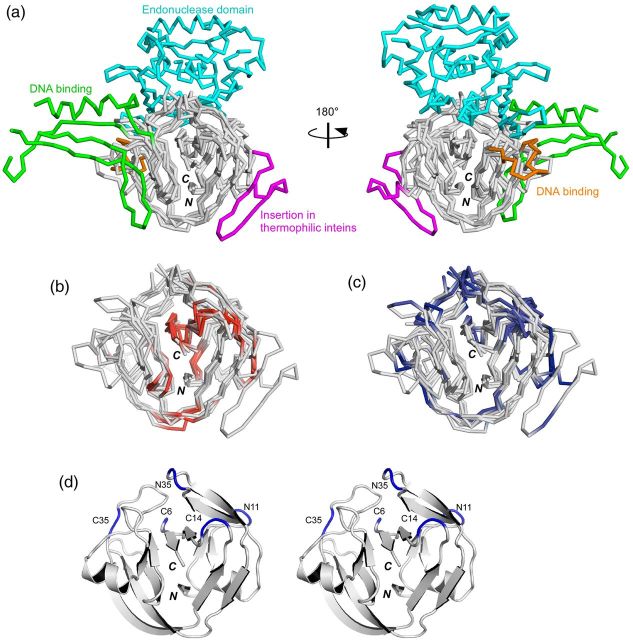
Fig. 2.
Locations of the reported split sites on the three-dimensional structures of inteins. (a) Four intein structures superimposed with the HINT fold (SceVMA intein (1LWS), SspDnaBΔ275 intein (1MI8), NpuDnaE intein (2KEQ), TvoVMAΔ21 intein (4O1S)). The endonuclease domain (residues 183–414, colored in cyan) and the DNA binding domains (residues 54-69 and 86-156, colored respectively in orange and green) of SceVMA intein are displayed. The insertion found in thermophilic inteins is displayed in magenta (residues 28-51 in TvoVMA intein). (b) The split sites corresponding to the ‘inactive’ split inteins are colored red in the four superimposed structures, without showing the endonuclease and DNA binding domains. (c) The split sites corresponding to the ‘active’ split inteins are mapped in the same four structures in blue. (d) A stereoview of a ribbon drawing of NpuDnaE intein (2KEQ) with the five common split sites discussed in the text. N and C denote the N and C termini, respectively.