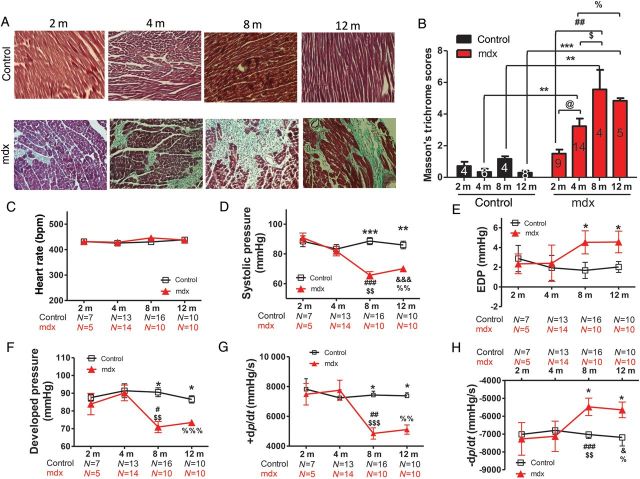
Figure 1.
Cardiac fibrosis starts at a young age (2 months) in mdx mice, but baseline cardiac dysfunction is only detected from 8 months onwards. (A) Images (×200) of Masson's trichrome staining of myocardial fibrosis (blue). (B) Fibrosis scores in ventricular tissue at different ages (2, 4, 8, and 12 months). (C–H) Systolic pressure (D), end-diastolic pressure (EDP; E), developed pressure (F), maximum +dp/dt (G), and minimum −dp/dt (H) determined by intra-LV haemodynamic measurements at the same heart rates (400–450 bpm, C) in control and mdx mice at different ages (2, 4, 8, and 12 months). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 control vs. mdx mice at the same age, respectively; @P < 0.05; 4- vs. 2-month-old mdx mice; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 for 8- vs. 2-month-old mdx mice; $$P < 0.01, $$$P < 0.001 for 8- vs. 4-month-old mdx mice; &P < 0.05, &&&P < 0.001 for 12- vs. 2-month-old mdx mice; %P < 0.05, %%P < 0.01, %%%P < 0.001 for 12- vs. 4-month-old mdx mice. Two-way ANOVAs with the post hoc test (Bonferroni adjustment) were performed. Numbers of animals examined are indicated in the bars (B) or underneath the age group (C–H).