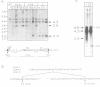
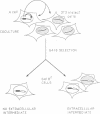
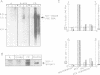
Abstract
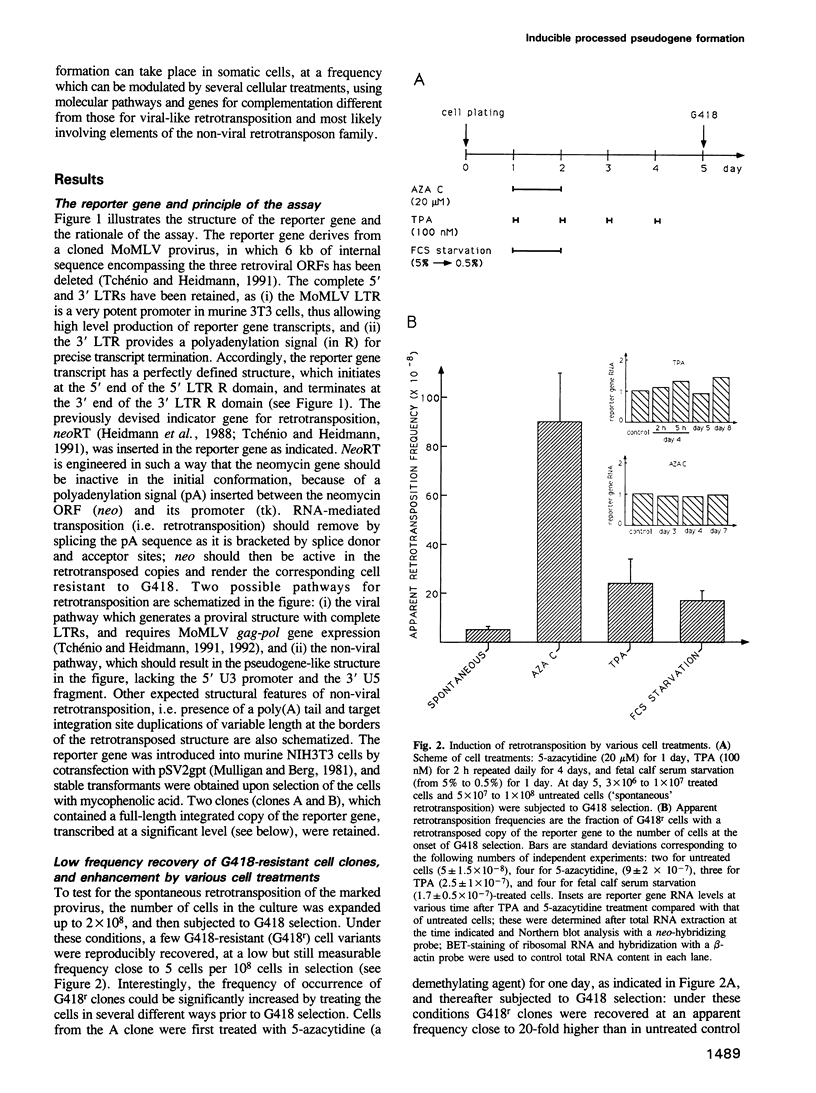
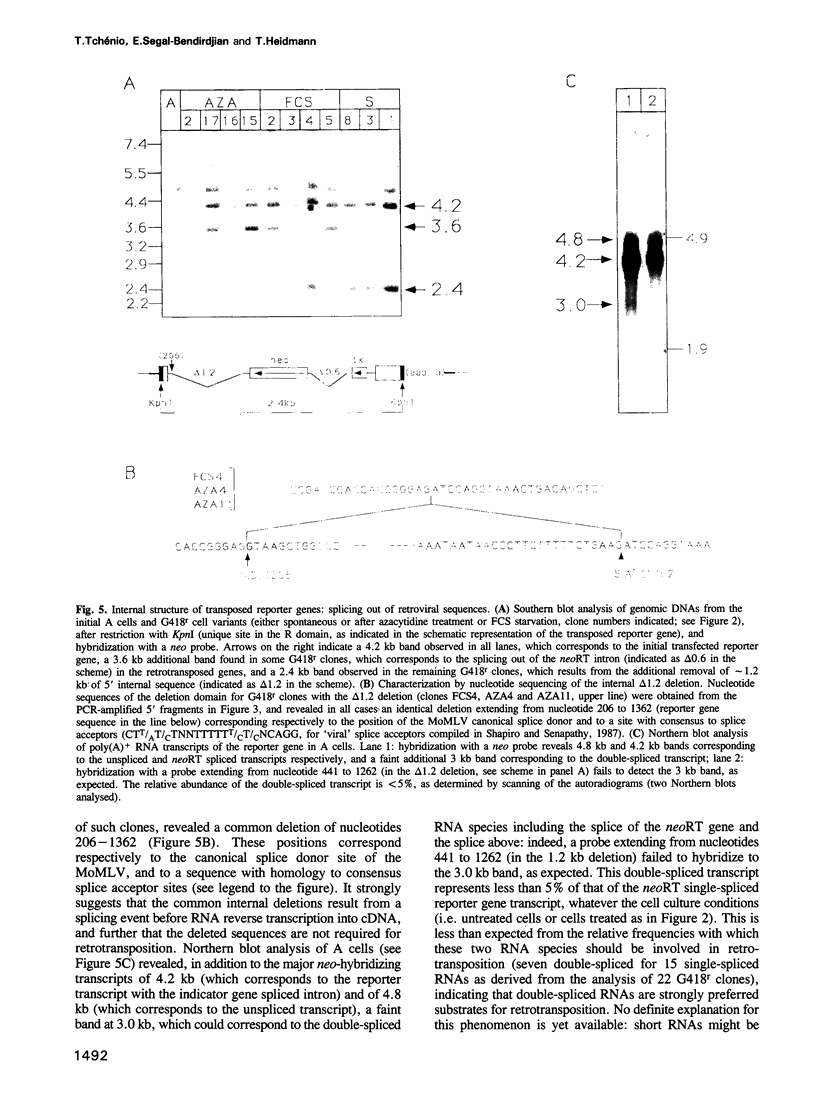
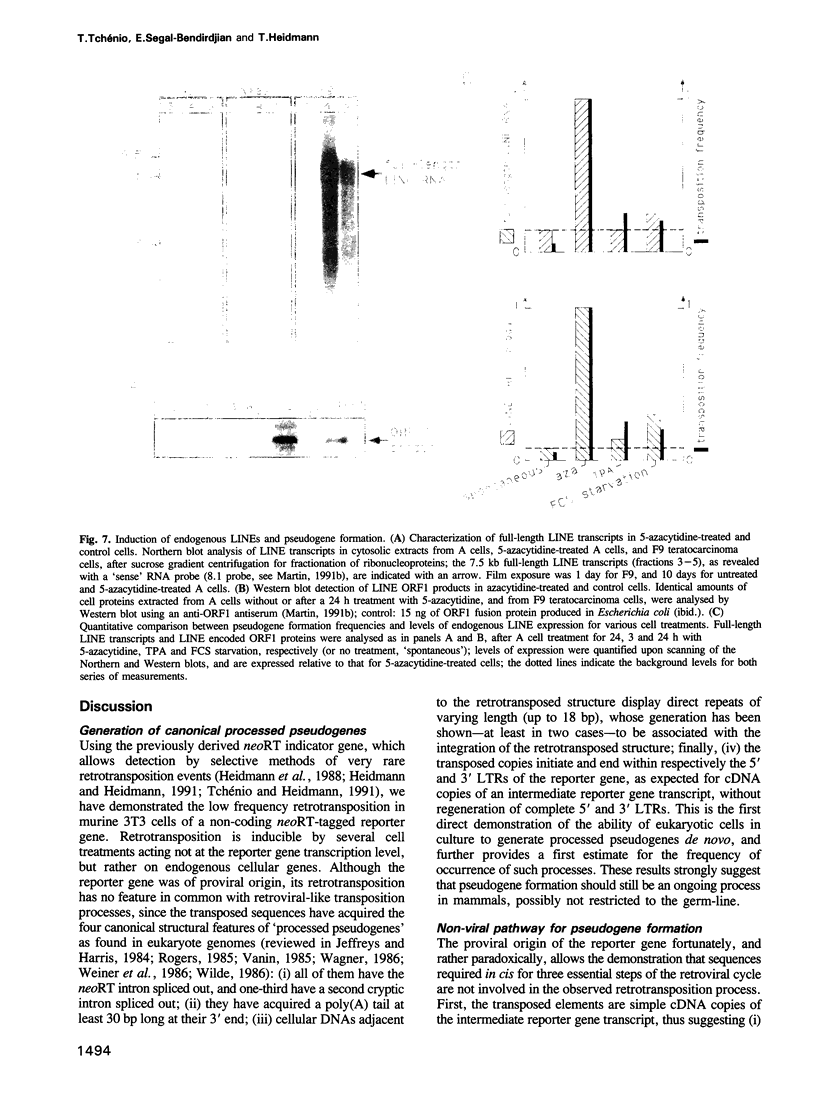
Using as a reporter gene a non-coding proviral structure marked with an intron-containing indicator, we demonstrate the de novo formation, via a retrotransposition pathway, of canonical processed pseudogenes in cultured mammalian cells. Their structural features include endings corresponding to the start and termination of the RNA intermediate, intron loss, acquisition of a 3' poly(A) tail, and target site duplications of variable length. The absence of extracellular intermediates for these processes, and the elimination during retrotransposition of sequences in the reporter gene essential in cis for a retroviral cycle, further suggest that endogenous retroviruses or related elements are not involved. Pseudogene formation frequency is markedly increased (up to 10-fold) by several treatments including treatment with 5-azacytidine or tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate, or serum starvation, which do not act at the reporter gene transcription level, but rather on endogenous genes--including the LINE elements--necessarily involved in trans-complementation for retrotransposition.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Retroviruses and retrotransposons: the role of reverse transcription in shaping the eukaryotic genome. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):481–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Corces V. G. Transcription and reverse transcription of retrotransposons. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:403–434. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnerot C., Rocancourt D., Briand P., Grimber G., Nicolas J. F. A beta-galactosidase hybrid protein targeted to nuclei as a marker for developmental studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6795–6799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H. DNA methylation and gene activity. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Cloyd M. W., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Cellular origin and role of mink cell focus-forming viruses in murine thymic lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):25–31. doi: 10.1038/295025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deragon J. M., Sinnett D., Labuda D. Reverse transcriptase activity from human embryonal carcinoma cells NTera2D1. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3363–3368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derr L. K., Strathern J. N., Garfinkel D. J. RNA-mediated recombination in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornburg R., Temin H. M. Presence of a retroviral encapsidation sequence in nonretroviral RNA increases the efficiency of formation of cDNA genes. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):886–889. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.886-889.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornburg R., Temin H. M. Retroviral vector system for the study of cDNA gene formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2328–2334. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornburg R., Temin H. M. cDNA genes formed after infection with retroviral vector particles lack the hallmarks of natural processed pseudogenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):68–74. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G., Singer M. F. LINE-1: a mammalian transposable element. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 8;910(3):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Mumm S. R. Unraveling retrovirus integration. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90707-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann O., Heidmann T. Retrotransposition of a mouse IAP sequence tagged with an indicator gene. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90217-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann T., Heidmann O., Nicolas J. F. An indicator gene to demonstrate intracellular transposition of defective retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2219–2223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov V. A., Melnikov A. A., Siunov A. V., Fodor I. I., Ilyin Y. V. Authentic reverse transcriptase is coded by jockey, a mobile Drosophila element related to mammalian LINEs. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2489–2495. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07788.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S., Heidmann T. An indicator gene for detection of germline retrotransposition in transgenic Drosophila demonstrates RNA-mediated transposition of the LINE I element. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1927–1937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Wong C., Youssoufian H., Scott A. F., Phillips D. G., Antonarakis S. E. Haemophilia A resulting from de novo insertion of L1 sequences represents a novel mechanism for mutation in man. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):164–166. doi: 10.1038/332164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibold D. M., Swergold G. D., Singer M. F., Thayer R. E., Dombroski B. A., Fanning T. G. Translation of LINE-1 DNA elements in vitro and in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6990–6994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine K. L., Steiner B., Johnson K., Aronoff R., Quinton T. J., Linial M. L. Unusual features of integrated cDNAs generated by infection with genome-free retroviruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1891–1900. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M. Creation of a processed pseudogene by retroviral infection. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90759-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. L. LINEs. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Dec;1(4):505–508. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. L. Ribonucleoprotein particles with LINE-1 RNA in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4804–4807. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias S. L., Scott A. F., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Boeke J. D., Gabriel A. Reverse transcriptase encoded by a human transposable element. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1808–1810. doi: 10.1126/science.1722352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki Y., Nishisho I., Horii A., Miyoshi Y., Utsunomiya J., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B., Nakamura Y. Disruption of the APC gene by a retrotransposal insertion of L1 sequence in a colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 1;52(3):643–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse B., Rotherg P. G., South V. J., Spandorfer J. M., Astrin S. M. Insertional mutagenesis of the myc locus by a LINE-1 sequence in a human breast carcinoma. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):87–90. doi: 10.1038/333087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Fiore D. Ordered interstrand and intrastrand DNA transfer during reverse transcription. Science. 1988 Aug 26;241(4869):1064–1069. doi: 10.1126/science.2457948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats A. C., Roy C., Wang P. A., Erard M., Housset V., Gabus C., Paoletti C., Darlix J. L. cis elements and trans-acting factors involved in dimer formation of murine leukemia virus RNA. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):774–783. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.774-783.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pélisson A., Finnegan D. J., Bucheton A. Evidence for retrotransposition of the I factor, a LINE element of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4907–4910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. The origin and evolution of retroposons. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:187–279. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain A., Coffin J. M. Mechanism of transduction by retroviruses. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):841–845. doi: 10.1126/science.1371365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchenio T., Heidmann T. Defective retroviruses can disperse in the human genome by intracellular transposition. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2113–2118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2113-2118.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchenio T., Heidmann T. High-frequency intracellular transposition of a defective mammalian provirus detected by an in situ colorimetric assay. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1571–1578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1571-1578.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Reverse transcription in the eukaryotic genome: retroviruses, pararetroviruses, retrotransposons, and retrotranscripts. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Nov;2(6):455–468. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F. Processed pseudogenes: characteristics and evolution. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:253–272. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. D. Pseudogenes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;19(4):323–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]