Figure 2.
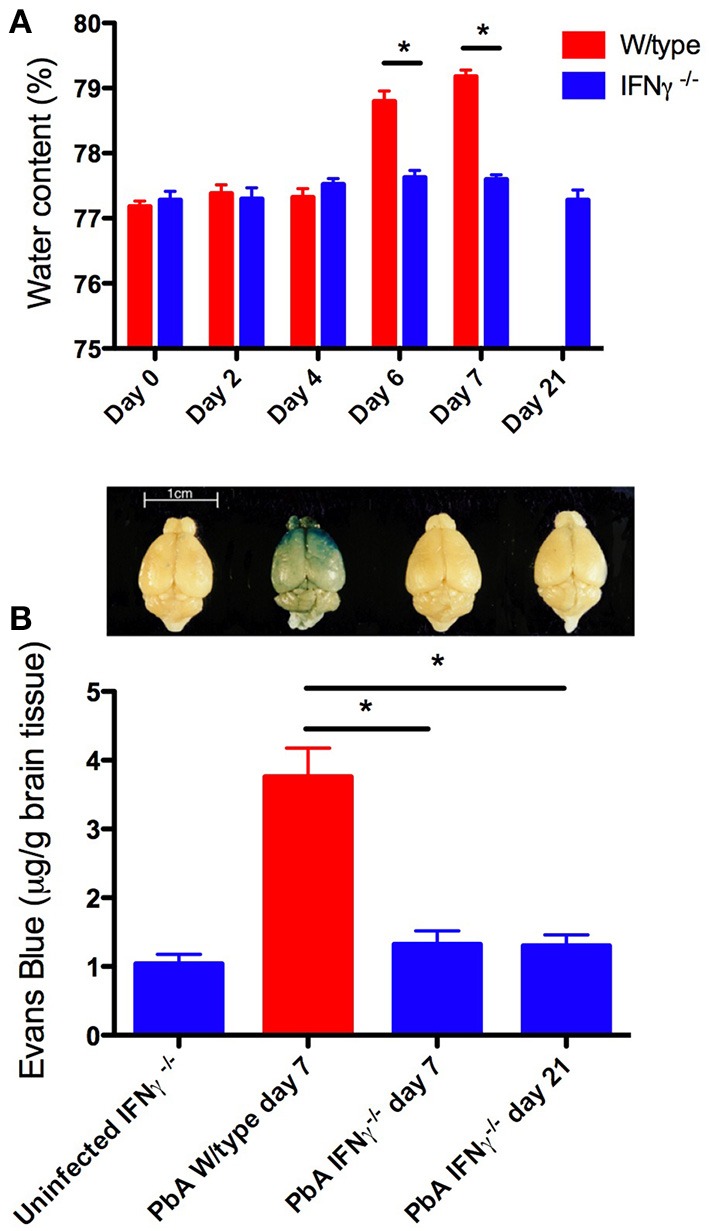
Brain edema and blood-brain barrier compromise after PbA infection. Water content was calculated from wet and dry weight. Evans blue, a dye that binds to circulating albumin, was injected intravenously 2 h before mice were euthanased; the brain was perfused with saline, removed, photographed, and water-extracted; the Evans blue content was measured spectrophotometrically at 510 nm. (A) PbA-infected wild-type mouse brains had significantly greater water content compared with infected IFN-γ−/− mice at days 6 and 7 post-inoculation (*p < 0.001, Two-Way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test). (B) PbA-infected wild-type mice had significantly greater extravasation of Evans Blue dye into the brain parenchyma on day 7 post-inoculation compared to infected IFN-γ−/− mice on day 7 or 21 post-inoculation (*p < 0.001, One-Way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test). Above each bar of the graph is shown a representative brain from that experimental group. Columns and vertical bars are mean ± s.e.m. (n = 5 per group).
