Figure 5.
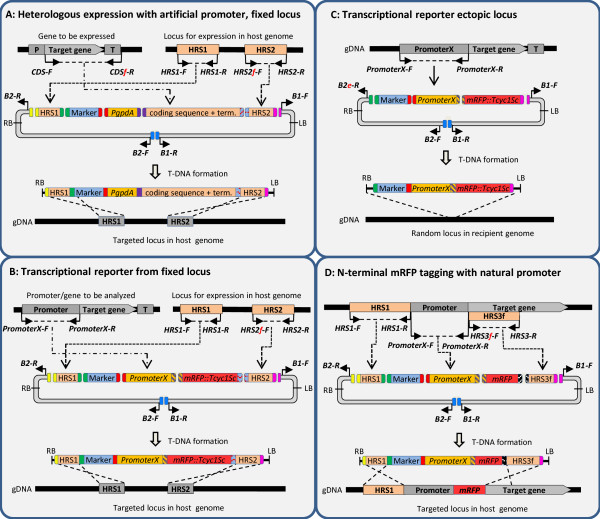
Design of vectors for heterologous expression (A), transcriptional report constructs (B and C) and N’terminal mRFP tagging (D). A) Heterologous expression of a gene of interest from a predefined locus in the genome. Note the unique overhangs on the HRS2f (targeted locus) and CDSf-R (gene to be expressed) fragments that allow for fusion of the two. B) Targeted integration of transcriptional reporter construct to monitor the expression of the gene of interest. C) Transcriptional reporter construct for random integration. D) N’terminal mRFP tagging of gene of interest. The promoter element in the setup can either be the gene’s natural promoter, which should be as short as possible to limit the change of recombination, or one of the heterologous promoters (PgpdA or PalcA). Primers are represented by solid black arrows. Aberrations: gDNA = genomic DNA; P = promoter; CDS = coding sequence; T = terminator; RB & LB = right & left borders defining the T-DNA region; T-DNA = transfer DNA.
