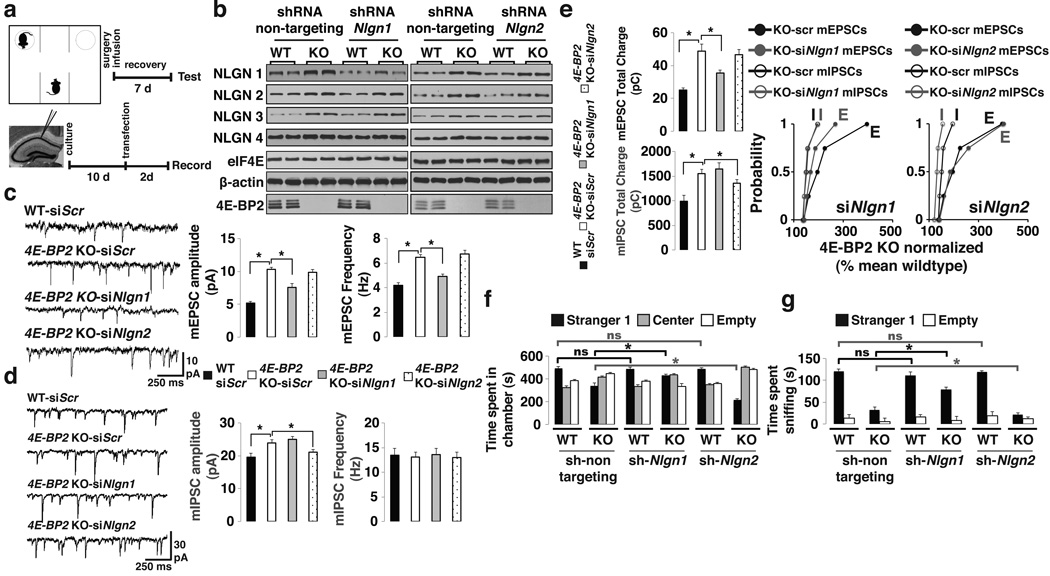
Figure 5. Knockdown of neuroligin 1 rescues the excitatory/inhibitory synaptic activity imbalance and social deficits in 4E-BP2-KO mice.
(a) Schematic of the three-chamber test in mice icv-injected with lentiviruses expressing shRNAs (Top) and recordings from siRNA-transfected slice-cultures (Bottom).
(b) Western blot analysis of hippocampal lysates from WT or 4E-BP2-KO mice injected with lentiviruses expressing shRNAs against a non-targeting sequence or Nlgn1-2. Extracts were probed for NLGN1-4, β -actin, eIF4E and 4E-BP2; n=4-quantification in Supplementary Fig. 16b,c.
(c,d) Effects of Nlgn1 or Nlgn2 knockdown on mEPSCs (c) or mIPSCs (d) amplitude and frequency in transfected pyramidal cells.
(e) mEPSCs (Top) or mIPSCs (Middle) total charge transfer in Nlgn1-2 knockdown cells. Bottom: Relative changes in mEPSC and mIPSC total charge transfer, normalized to the mean WT value, for each neuron from 4E-BP2-KO slices; Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. For c-e, n=5 per group; *p<0.05; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc.
(f,g) Knockdown of Nlgn1-2 in the three-chamber test showing (f) time spent in chambers and (g) time spent sniffing the wire-cage.
For f–g, n=12 per group; *p<0.02; two-way ANOVA, with a Bonferroni’s post-hoc. Error-bars mean ±SEM.