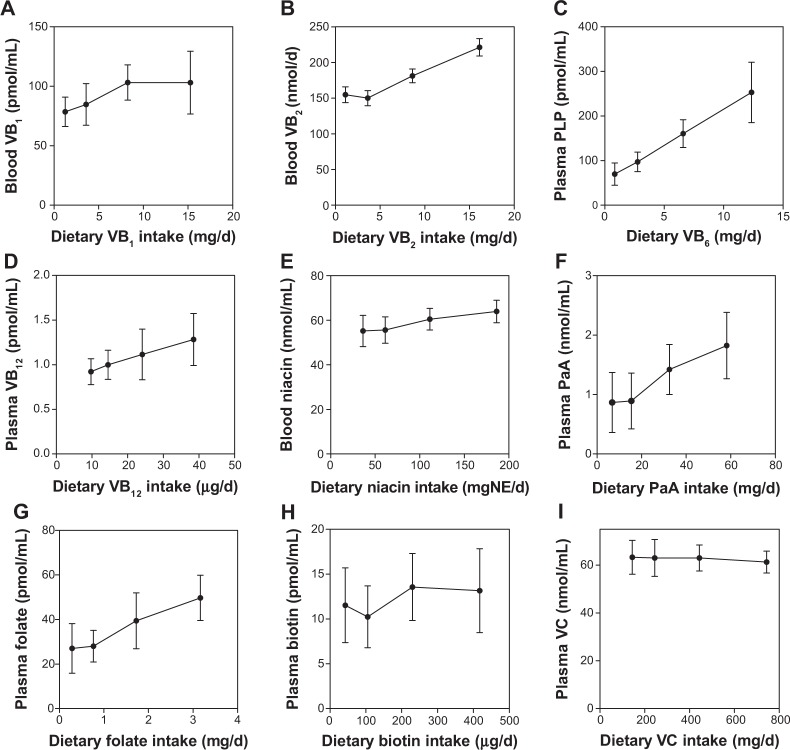
Figure 2.
Correlation of vitamin intake and concentration of water-soluble vitamins in the blood of the Japanese male subjects.
Notes: Each point represents the mean ± SD of the 10 subjects. Pearson coefficients were calculated to determine the correlation between vitamin intake and the vitamin concentration in the blood or urine. (A) VB1 = vitamin B1 (r = 0.888, p = 0.0581; not significant); (B) VB2 = vitamin B2 (r = 0.976, p = 0.024; significant); (C) PLP, a coenzyme form of vitamin B6 (r = 1.000, p = 0.0002; significant); (D) VB12 = vitamin B12 (r = 0.999, p = 0.002; significant); (E) nicotinamide (r = 0.984, p = 0.016; significant); (F) PaA = pantothenic acid (r = 0.984, p = 0.016; significant); (G) folate (r = 0.989, p = 0.011; significant); (H) biotin (r = 0.713, p = 0.289; not significant); (I) VC = vitamin C (r = −0.927, p = 0.074; not significant).