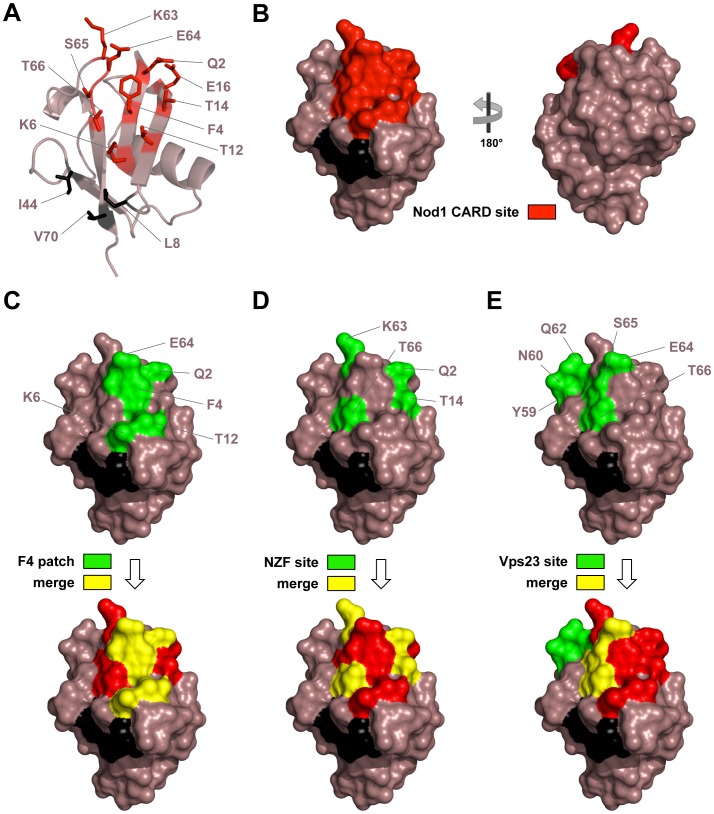
Figure 3. Identified UBD binding sites in Ub.
Ub is colored in mauve taupe. A) Cartoon representation of Ub. Residues mediating interaction with NOD1 CARD are shown as sticks and are colored red. The canonical hydrophobic pocket residues are shown as sticks and colored black. B) Surface views of the NOD1 CARD interaction site on Ub. C) Surface views of the Phe4 hydrophobic patch (F4 patch) on Ub alone (green) and merged with the NOD1 CARD site (yellow). D) Surface views of one site on Ub recognized by the NZF domain of HOIL-1L alone (green) and merged with the NOD1 CARD site (yellow). This domain specifically recognizes linear chains of Ub by binding to the hydrophobic pocket of the distal Ub and to an area surrounding Phe4 of the proximal Ub of a linear di-Ub moiety. Residues on the proximal Ub interacting within 3.6 Å of the NZF domain in a crystal structure of its complex with linear di-Ub (PDB ID: 3B08) are shown. E) Surface views of a second site on Ub recognized by the Vps23 UEV domain (Vps23 site) alone (green) and merged with the NOD1 CARD site (yellow). The Vps23 UEV domain binds both the hydrophobic pocket and this second site on Ub. Residues on Ub interacting within 3.6 Å of the UEV domain in a crystal structure of its complex with mono-Ub (PDB ID: 1UZX) are shown.