Figure 1.
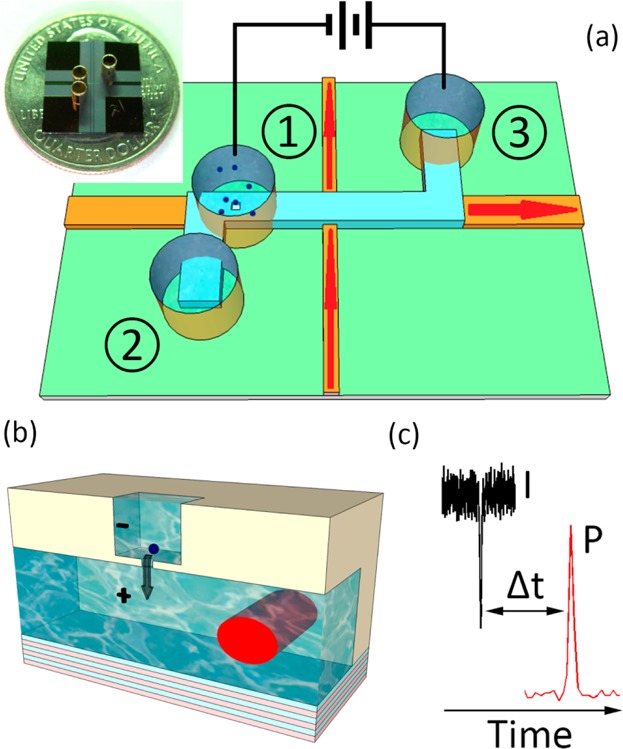
Nanopore-gated optofluidic device. (a) Schematic view of intersecting solid-core (orange) and liquid-core (blue) optical waveguides on a silicon chip with particles and electrodes in metal reservoirs. The inset shows a photograph of chip. (b) Schematic view of particle translocation through a nanopore milled into the bottom of a silicon dioxide layer; the red area shows the optical excitation volume defined by the fwhm area of the optical waveguide mode traversing the liquid core. (c) Principle of dual-mode electro-optical single-molecule detection, in which each particle produces two characteristic signals, a transient current decrease and a fluorescence spike, separated by a characteristic time Δt.
