Figure 1. Inhibition of MafA expression in β-cell lines or mouse islets resulted in reduced expression of Prlr and Ccnd2.
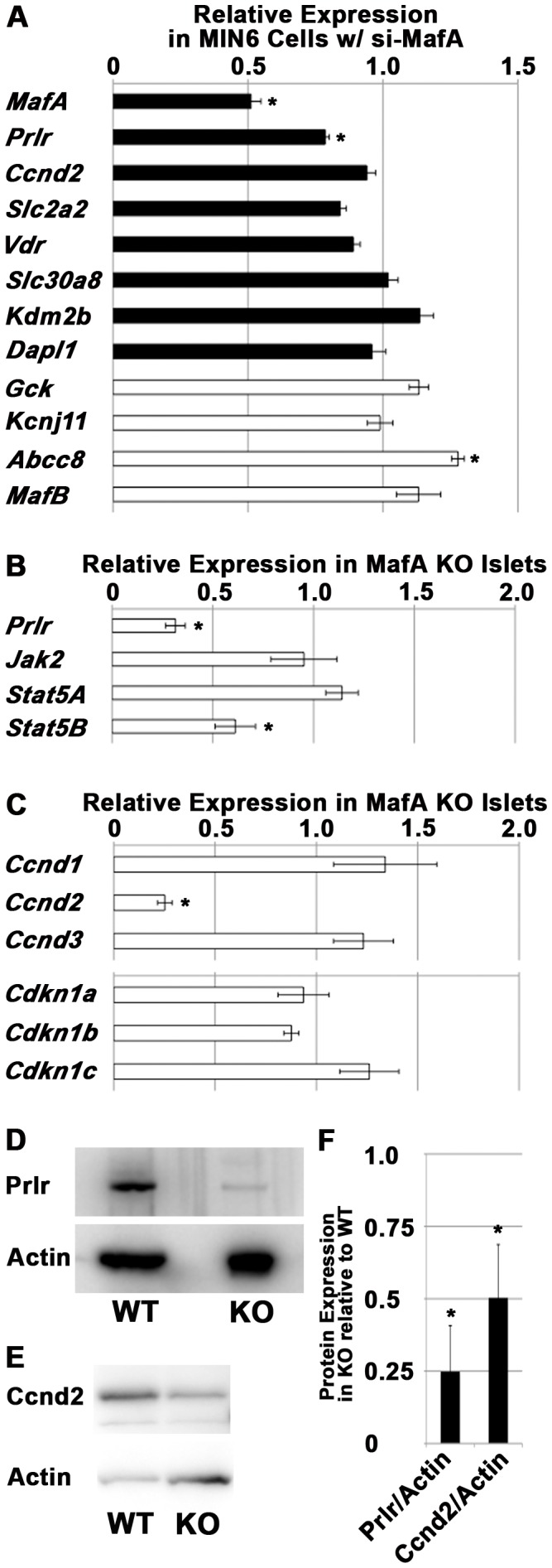
(A) mRNA expression of the indicated molecules in MIN6 cells transfected with MafA siRNA relative to cells transfected with control siRNA. n = 4 for each molecule, except n = 3 for MafB. Black bars: molecules detected in the transcriptome of MafA KO islets; white bars: molecules involved in β-cell function. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of prolactin signaling components in MafA KO islets relative to wild-type islets. n = 5 for Prlr; n = 3 for Jak2, Stat5A and Stat5B. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of molecules involved in the cell cycle in MafA KO islets relative to wild-type islets. n = 4 for Ccnd1; n = 5 for Ccnd2 and Ccnd3; n = 3 for Cdkn1a, Cdkn1b and Cdkn1c. (D) Immunoblots of Prlr and actin in wild-type (WT) and MafA KO (KO) islets. n = 3. (E) Immunoblots of Ccnd2 and actin in wild-type (WT) and MafA KO (KO) islets. n = 3. (F) Quantification of the results of (D) and (E). The data represent the mean ± S.E.M. in (A), (B), (C) and (F), and representative results are shown in (D) and (E). Asterisks means p<0.05.
