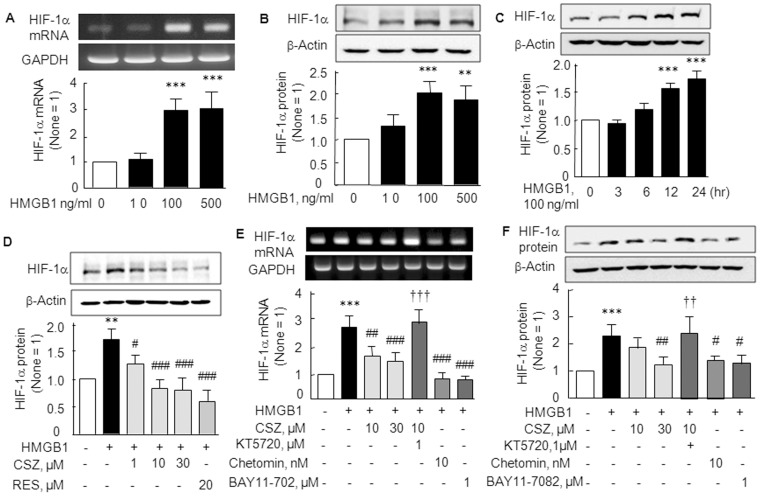
Figure 2. Elevations of HIF-1α mRNA and protein expressions by HMGB1 and their inhibition by cilostazol.
(A and B) Concentration-dependent HMGB1 (10–500 ng/ml)-induced increases in the mRNA and protein expressions of HIF-1α. (C) Time (3, 6, 12, and 24 hr)-dependent increases in HIF-1α protein levels in the presence of 100 ng/ml of HMGB1. (D) Concentration-dependent decrease of HMGB1 (100 ng/ml)-induced HIF-1α protein by cilostazol (CSZ; 1, 10 and 30 µM) and resveratrol (RES, 20 µM). (E and F) Reverse of cilostazol-induced decrease in HIF-1α mRNA (E) and protein (F) by KT5720 (1 µM; a cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor), and significant suppression of HMGB1-induced HIF-1α mRNA by chetomin (10 nM, an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible transcription) and by Bay11–7082 (1 µM, an inhibitor of IκBα phosphorylation). Results are the means ±SEM of 4–5 experiments. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs. no treatment; # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs. HMGB1 alone; ††† P<0.001 vs. 10 µM cilostazol.