Abstract
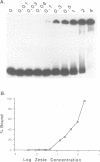
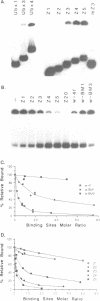
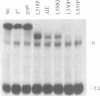
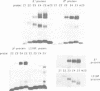
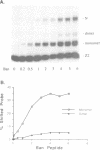
The Drosophila zeste protein forms multimeric species in vitro through its C-terminal domain. Multimerization is required for efficient binding to DNA containing multiple recognition sequences and increasing the number of binding sites stimulates binding in a cooperative manner. Mutants that can only form dimers still bind to a dimeric site, but with lower affinity. Mutations or progressive deletions from the C-terminal show that when even dimer formation is prevented, DNA-binding activity is lost. Surprisingly, binding activity is regained with larger deletions that leave only the DNA-binding domain. Additional protein sequences apparently inhibit DNA binding unless they permit multimerization. The DNA-binding domain peptides bind strongly even to isolated recognition sequences and they bind as monomers. The ability of various zeste peptides to stimulate white gene expression in vivo shows that multimeric forms are the functional species of the zeste product in vivo. The DNA-binding domain peptide binds well to DNA in vitro, but it cannot stimulate white gene expression in vivo. This failure may reflect the need for an activation domain or it may be caused by indiscriminate binding of this peptide to non-functional isolated sites. Multimerization increases binding specificity, selecting only sites with multiple recognition sequences.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson M., Pirrotta V. The Drosophila zeste protein binds cooperatively to sites in many gene regulatory regions: implications for transvection and gene regulation. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3907–3915. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M., Pirrotta V. The product of the Drosophila zeste gene binds to specific DNA sequences in white and Ubx. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1387–1392. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02379.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickel S., Pirrotta V. Self-association of the Drosophila zeste protein is responsible for transvection effects. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2959–2967. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07488.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Bickel S., Benson M., Pirrotta V., Tjian R. Zeste encodes a sequence-specific transcription factor that activates the Ultrabithorax promoter in vitro. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):713–722. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Zachar Z. Evidence that two mutations, wDZL and z1, affecting synapsis-dependent genetic behavior of white are transcriptional regulatory mutations. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):819–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. D., Chan C. S., Pirrotta V. Conserved DNA binding and self-association domains of the Drosophila zeste protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):598–608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croston G. E., Kerrigan L. A., Lira L. M., Marshak D. R., Kadonaga J. T. Sequence-specific antirepression of histone H1-mediated inhibition of basal RNA polymerase II transcription. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):643–649. doi: 10.1126/science.1899487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelbart W. M. Synapsis-dependent allelic complementation at the decapentaplegic gene complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2636–2640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Green M. M., Corces V. G. Tissue-specific transcriptional enhancers may act in trans on the gene located in the homologous chromosome: the molecular basis of transvection in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2247–2256. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. W., Judd B. H. Allelic pairing and gene regulation: A model for the zeste-white interaction in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1368–1372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman T. C., Tasaka S. E., Suzuki D. T. The interaction of two complex loci, zeste and bithorax in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1973 Oct;75(2):299–321. doi: 10.1093/genetics/75.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laney J. D., Biggin M. D. zeste, a nonessential gene, potently activates Ultrabithorax transcription in the Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1531–1541. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Zimm B. H. Understanding the anomalous electrophoresis of bent DNA molecules: a reptation model. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):396–399. doi: 10.1126/science.2756426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschytz E., Green M. M. The zeste-white interaction: induction and genetic analysis of a novel class of zeste alleles. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):999–1002. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01919.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansukhani A., Crickmore A., Sherwood P. W., Goldberg M. L. DNA-binding properties of the Drosophila melanogaster zeste gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):615–623. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan D. J., Huang J. D., Courey A. J. Functional analysis of the Drosophila twist promoter reveals a dorsal-binding ventral activator region. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1892–1901. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Bickel S., Mariani C. Developmental expression of the Drosophila zeste gene and localization of zeste protein on polytene chromosomes. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1839–1850. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V. The genetics and molecular biology of zeste in Drosophila melanogaster. Adv Genet. 1991;29:301–348. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian S., Varjavand B., Pirrotta V. Molecular analysis of the zeste-white interaction reveals a promoter-proximal element essential for distant enhancer-promoter communication. Genetics. 1992 May;131(1):79–90. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastelli L., Chan C. S., Pirrotta V. Related chromosome binding sites for zeste, suppressors of zeste and Polycomb group proteins in Drosophila and their dependence on Enhancer of zeste function. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1513–1522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05795.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. A transposable P vector that confers selectable G418 resistance to Drosophila larvae. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):167–171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. Expression of the Drosophila white gene under the control of the hsp70 heat shock promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3765–3772. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. T., Goldberg M. L. The Drosophila zeste gene and transvection. Trends Genet. 1989 Jun;5(6):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]