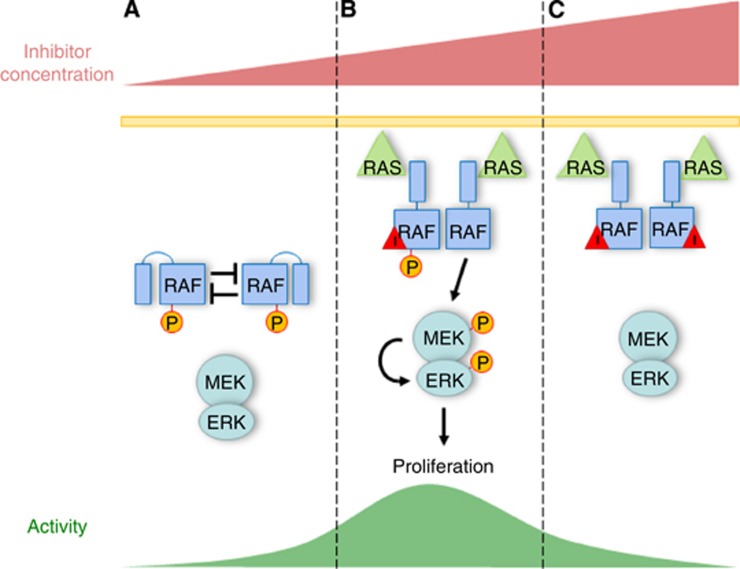
Figure 1.
Role of inhibitory autophosphorylation in paradoxical activation by RAF kinase inhibitors. (A) RAF kinase activity is held in check through inhibitory autophosphorylation, potentially in trans, in RAF dimers. (B) Low concentration of a small-molecule RAF kinase inhibitor inhibits one RAF protomer, preventing it from phosphorylating the other protomer. The combination of loss of inhibitory phosphorylation and allosteric effects between the two RAF protomers results in increased kinase activity. (C) At higher concentrations the RAF kinase inhibitor binds and inhibits both RAF protomers and kinase activity is decreased.