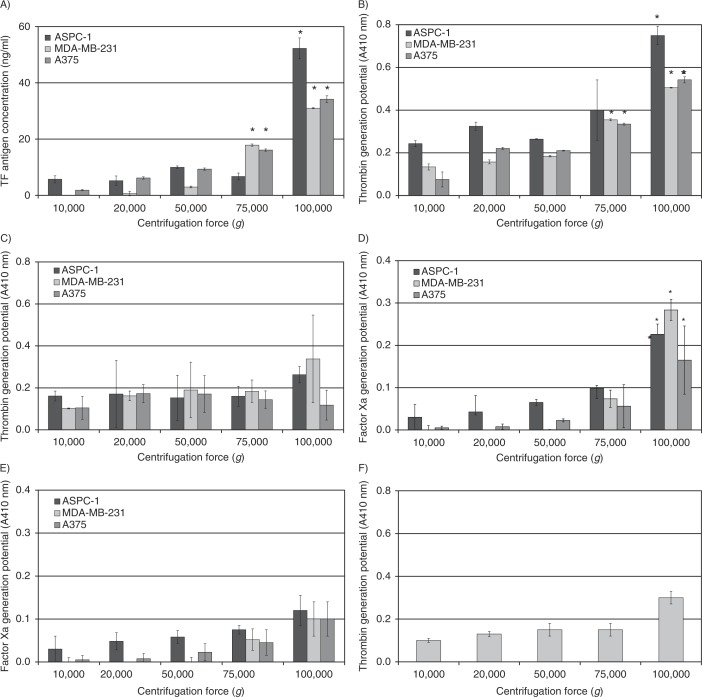
Fig. 1.
Analysis of TF antigen and activity associated with microvesicles isolated at various RCF. Cell lines (AsPC-1, MDA-MB-231 and A375) were washed and pre-adapted to respective serum-free media prior to activation with PAR2-AP (SLIGRL; 20 µM). The conditioned media were collected and cleared of any cell debris by centrifuging at 5,400g for 10 min on a microcentrifuge. Cell-derived microvesicles were then sedimented at various RCF ranging from 20,000 to 100,000g at 20°C for 1 h. (A) TF antigen content of the recovered microvesicles was determined using a TF-specific EIA assay (n=3, *=p<0.05 vs. respective values recovered at 20,000g). TF-dependent and TF-independent thrombin generation potential of the fractions was assessed using a chromogenic thrombin generation assay in the presence (B) and absence of factor VII (C), respectively, by measuring the absorption at 410 nm (n=3, *=p<0.05 vs. respective values recovered at 20,000g). In addition, TF-dependent and TF-independent factor Xa generation potential of the samples was analysed using the Actichrome TF-activity assay in the presence (D) and absence of factor VII (E), respectively, by measuring the absorption at 410 nm (n=3, *=p<0.05 vs. respective values recovered at 20,000g). (F) Samples of microvesicles were isolated at various RCF ranging from 20,000 to 100,000g at 20°C for 1 h from the media of the MDA-MB-231 cell line and were pre-incubated with an inhibitory anti-TF antibody (HTF-1) prior to analysing the thrombin generation potential (n=3).