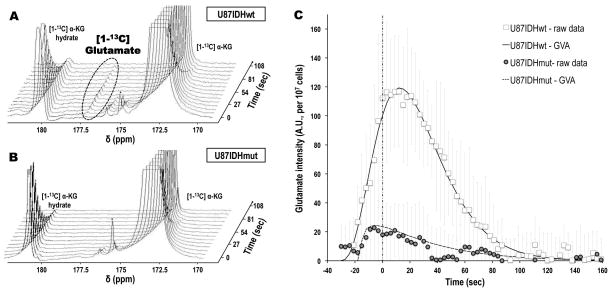
Figure 2. Hyperpolarized [1-13C] glutamate formation from hyperpolarized [1-13C] α-KG can be detected in live cells, and is decreased in U87IDHmut cells as compared to U87IDHwt.
Stack plots of dynamic 13C MR spectra acquired at 11.7 Tesla following injection of hyperpolarized [1-13C] α-KG in live U87IDHwt (A) and U87IDHmut (B) perfused cells (temporal resolution 9 seconds), showing the formation of hyperpolarized [1-13C] glutamate in U87IDHwt cells. Note the absence of detectable hyperpolarized [1-13C] glutamate in U87IDHmut cells. (C) Intensities of hyperpolarized [1-13C] glutamate in U87IDHwt (□) and U87IDHmut (
 ) perfused cells, showing the significantly higher level of glutamate in U87IDHwt cells as compared to U87IDHmut. Also of importance is the delayed formation of hyperpolarized [1-13C] glutamate versus the time of maximum hyperpolarized [1-13C] α-KG (vertical dashed line), as expected when metabolism occurs. The fit derived from the gamma-variate analysis (GVA) is displayed as a continuous line for U87IDHwt and as a dashed line for U87IDHmut perfused cells.
) perfused cells, showing the significantly higher level of glutamate in U87IDHwt cells as compared to U87IDHmut. Also of importance is the delayed formation of hyperpolarized [1-13C] glutamate versus the time of maximum hyperpolarized [1-13C] α-KG (vertical dashed line), as expected when metabolism occurs. The fit derived from the gamma-variate analysis (GVA) is displayed as a continuous line for U87IDHwt and as a dashed line for U87IDHmut perfused cells.