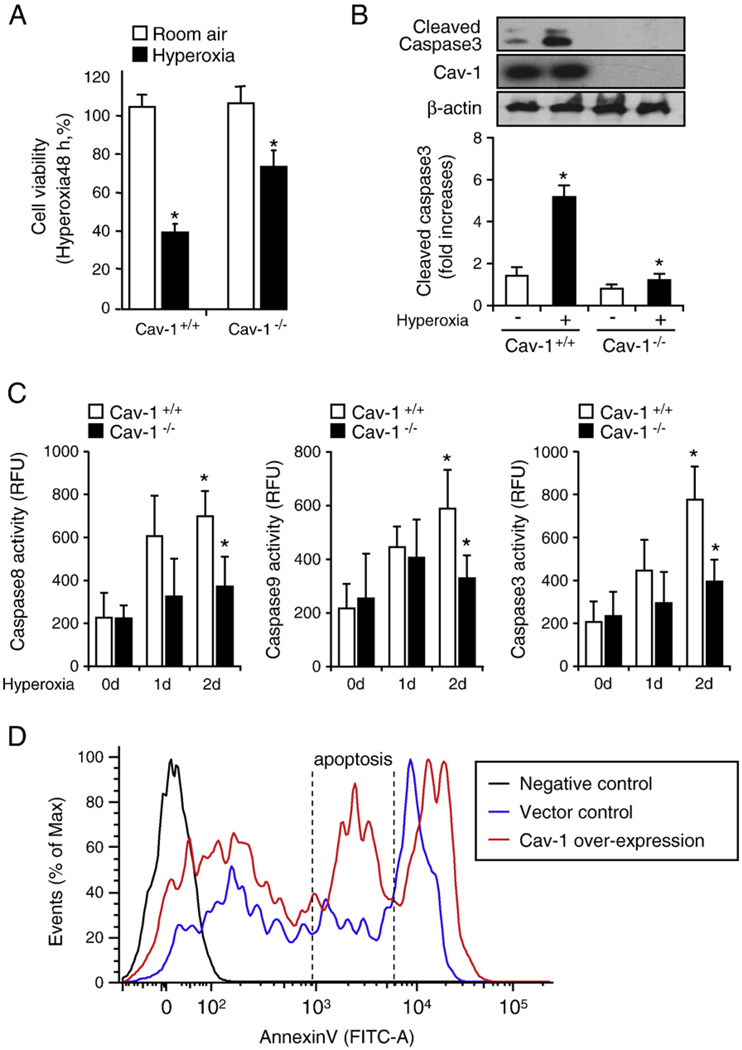
Fig. 1.
Deletion of Cav-1 protected lung epithelial cells against hyperoxia-induced apoptosis via the regulation of apoptotic pathways. Primary mouse lung epithelial cells were used in these experiments. Cells were exposed to room air (i.e., 20.8% oxygen + 78.08% nitrogen) or hyperoxia (95% oxygen + 5% balanced nitrogen) conditions. At designated times (i.e., after 4, 24, and 48 h), cells were collected and subjected to cell survival assays, namely, Western blot analysis or caspase activity assay. (A) The deletion of Cav-1 protected the primary mouse lung epithelial cells from hyperoxia-induced cell death. Primary mouse lung epithelial cells were isolated from either wild-type C57BL/6 mice (Cav-1+/+) or Cav-1−/− mice. The cells were then exposed to room air or hyperoxia conditions. After 48 h, cell viability was determined, as described under Materials and methods. (B) The deletion of Cav-1 protected the primary mouse lung epithelial cells against hyperoxia-induced activation of caspase 3. The epithelial cells were isolated from either wild-type C57BL/6 mice or Cav-1−/− mice. The cells were then exposed to hyperoxia conditions (48 h), after which cell lysates were obtained and subjected to Western blot analysis. (C) The deletion of Cav-1 protected the primary mouse lung epithelial cells against hyperoxia-induced caspase 3, 8, and 9 activation. Cells were exposed to room air, 24 h hyperoxia, or 48 h hyperoxia conditions. After exposure, cell lysates were obtained and caspase activities were measured using assays as described previously [40,41]. (D) To confirm the proapoptotic effect of Cav-1, we overexpressed Cav-1 or empty vectors in Beas-2B cells. Cell death was analyzed using FACS. Live cells were directly stained with annexin V–FITC and Sytox green dye. The Sytox green dye is impermeative to live cells and apoptotic cells, but stains necrotic cells with intense green fluorescence. After staining, apoptotic cells show green fluorescence, whereas dead cells show a higher level of green fluorescence and live cells show little or much lower levels of fluorescence. Three cell populations were observed, including (1) live cells, (2) apoptotic cells, and (3) necrotic cells. All experiments presented were repeated using three independent assays with similar results. *P<0.05.