Figure 4. Phosphatidylserine is necessary for uPAR-mediated internalization of apoptotic cells.
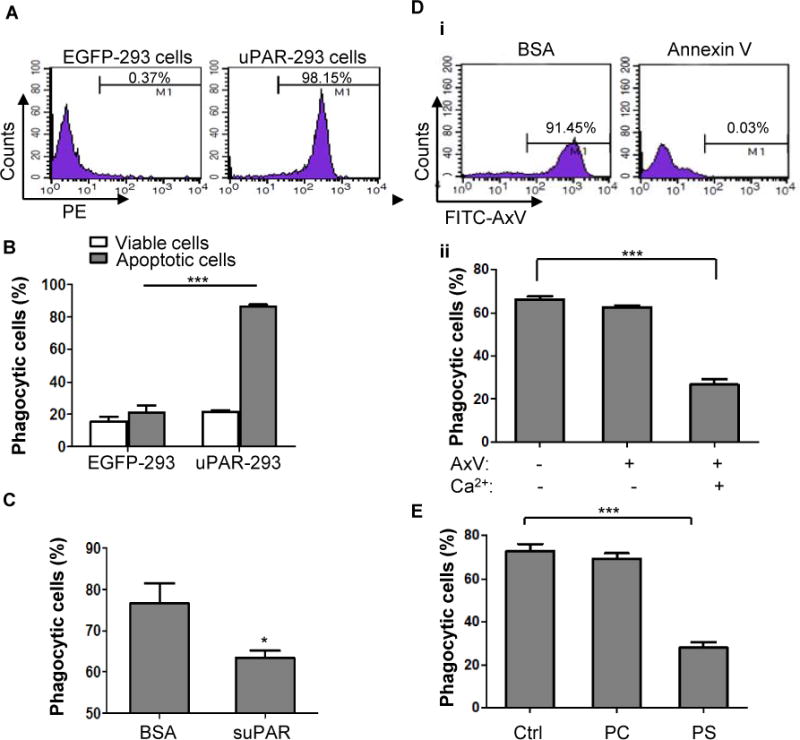
(A) HEK293 cells were transfected with pIRES2-EGFP plasmid (EGFP-293 cells) or IRES2-EGFP-uPAR plasmid (uPAR-293 cells), their expression of uPAR on membrane was measured by flow cytometry. (B) EGFP-293 cells and uPAR-293 cells were incubated with PKH26-labeled viable or apoptotic cells for 2 hours, respectively. Phagocytosis by green fluorescent 293 cells was evaluated after treatment with TB as described in the legend for Figure 1. ***, p<0.001. (C) suPAR inhibits phagocytosis of apoptotic cells in uPAR-293 cells. uPAR-293 cells were incubated with PKH26-labeled apoptotic cells in the presence of 1 μg/mL suPAR or BSA for 2 hours, which were subjected to the phagocytosis assay. *, p <0.05.(D) After preincubation with 50 μg/mL of unlabeled annexin V or BSA plus 2.5 mM CaCl2 for 20 minutes, apoptotic cells were labeled with FITC-conjugated annexin V (FITC-AxV), followed by flow cytometric analysis (i). After preincubation with 50 μg/mL of unlabeled annexin V in the presence or absence of 2.5 mM CaCl2 for 20 minutes, apoptotic cells were co-cultured with uPAR-293 cells, followed by treatment with TB and internalization analysis using flow cytometry (ii). ***, p < 0.001. (E) After preincubation with PBS (Ctrl), 50 nM PC liposome or PS liposome for 20 minutes, apoptotic cells were co-cultured with uPAR-293 cells, followed by treatment with TB and internalization analysis using flow cytometry.***, p < 0.001.
