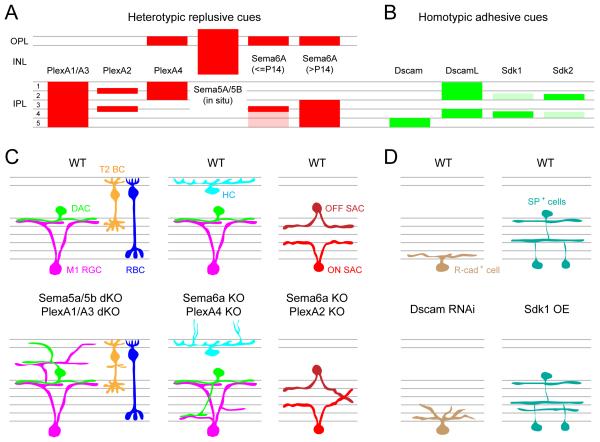
Figure 10. Molecular cues guiding retinal lamination.
(A-B) Schematic showing the expression pattern of heterotypic repulsive (mouse, A) and homotypic adhesive (chick, B) molecular cues across different laminae of the retina. Expression for Sema5A/5B revealed by in situ hybridization, and expression for all other molecules was determined by immunolabeling.
(C) Illustration showing aberrant lamination of mouse retinal cell types when semaphorin (Sema)-plexin (Plex) signaling is disrupted compared to wildtype retina (WT). KO: knockout, dKO: double knockout, M1 RGC: Type 1 melanopsin positive ganglion cell, DAC: dopaminergic amacrine cell, T2 BC: Type 2 OFF-cone bipolar cells, RBC: rod bipolar cell, HC: horizontal cell and SAC: starburst amacrine cell.
(D) Schematic showing disrupted dendritic lamination of R-cadherin (R-cad+) positive ganglion cell in the Dscam knockdown (by RNAi) retina, and unusual lamination of substance P positive (SP+) amacrine cells in sidekick1 (Sdk1) over-expressing (OE) chick retina.
Summarized from Matsuoka et al., 2011a; Matsuoka et al., 2012; Matsuoka et al., 2011b; Sun et al., 2013; Yamagata and Sanes, 2008, 2012; Yamagata et al., 2002.