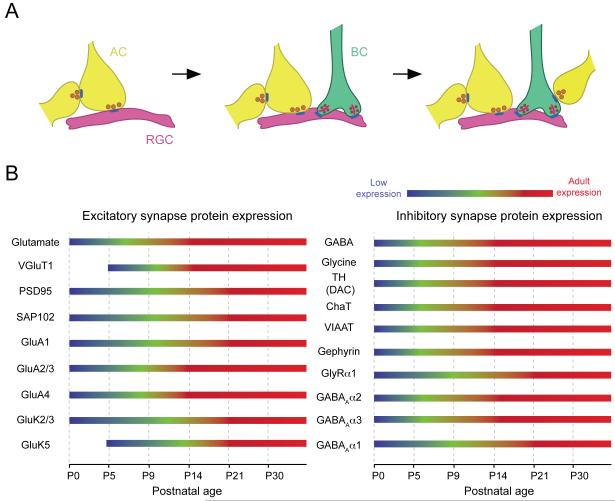
Figure 15. Synapse assembly in the IPL.
(A) Sequential development of synapses in the IPL. Amacrine cells (ACs) first establish contact with dendrites of retinal ganglion cells (RGC) and other amacrine cells. Next, bipolar cell (BC) terminals synapse onto ganglion cells. Thereafter, presynaptic inhibition provided by amacrine cells is established at the axon terminals of bipolar cells (see text for details).
(B) Relative expression levels of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic proteins at different time-points in the IPL from immunolabeling experiments carried out in rodent retina (summarized from: Fletcher and Kalloniatis, 1997; Guo et al., 2009; Hack et al., 2002; Johnson et al., 2003; Kim et al., 2000; Koulen, 1999; Sassoe-Pognetto and Wässle, 1997; Witkovsky et al., 2005). The color gradients are representative of the total expression of the synaptic proteins, rather than their distribution pattern. Note for synaptic proteins mediating excitatory neurotransmission AMPA (GluA1-4) receptors seem to be expressed prior to Kainate (GluK2/3 and GluK5) receptors in the developing IPL. On the other hand, inhibitory neurotransmitters GABA and glycine seem to be expressed at a similar timeline. The receptors mediating inhibitory neurotransmission, however, reach adult expression levels at different time-points with GABAAα2 and GABAAα3 receptors preceding GABAAα1 and GlyRα1 receptors.