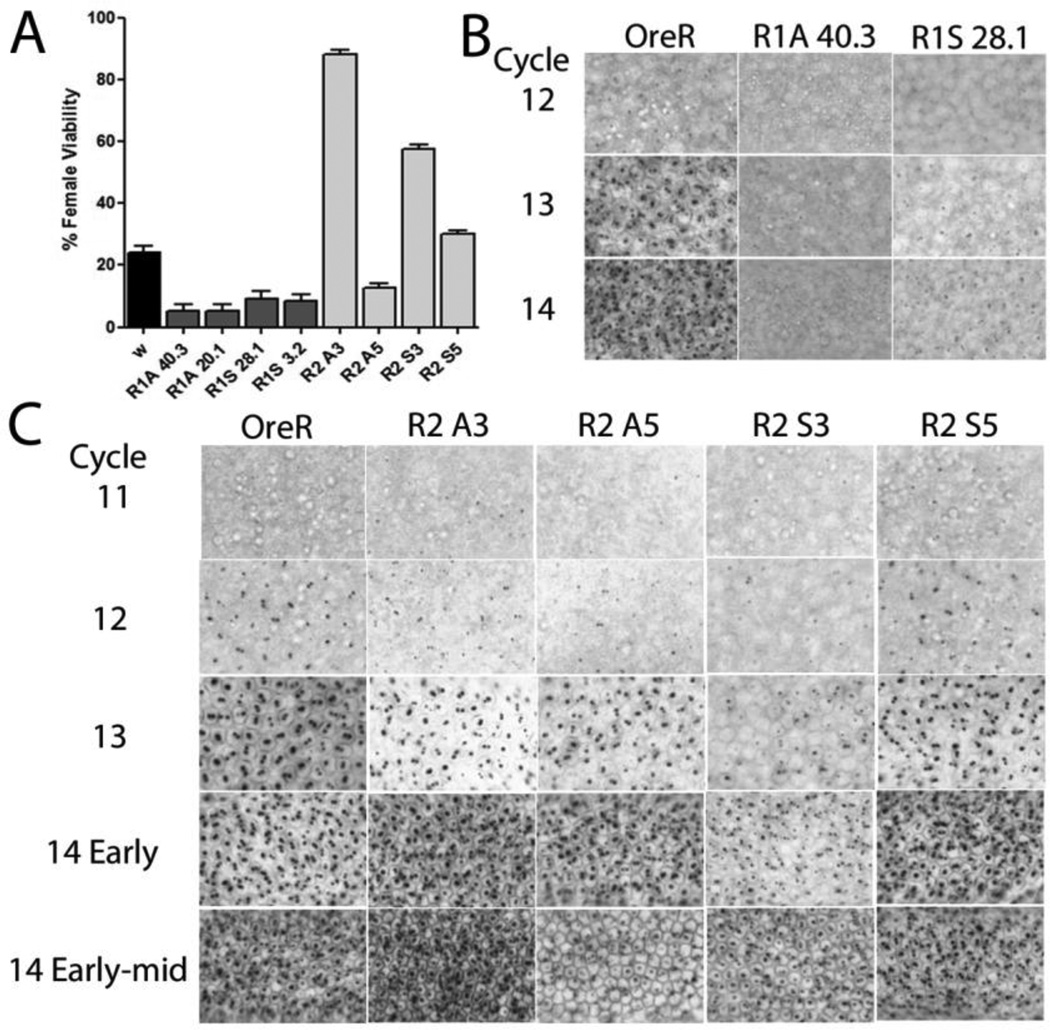
Figure 2. Constructs ectopically expressing R1 and R2 lncRNAs affect SxlPe.
(A)Altered female viability induced by ectopic expression of lncRNAs. Viability of eclosed females relative to males expressed as a percent. Mothers homozygous for the indicated lncRNA line were crossed to males with decreased sis-a, b numerator dose. w is w1118 and is the wild-type control (black bar), female viability ~24%. Error bars show percent +/− %SE. (B, C) Ectopic expression of lncRNAs affects SxlPe expression as shown by in situ hybridization of SxlPe transcripts, normally seen as two dots on each of the two X chromosomes as Sxl is on the X. Nuclear cycle number is shown on the left (Cycles 11–14 correspond with ~90–200min after egg laying), genotype at top. OreR is wild-type where the promoter is only on in females from cycle 12 to 14. in situs of R1 lines (B) show weaker staining dots (additional R1 lines in Fig. S2A), and R2 lines (C) which have more varied expression patterns and match the genetics in (A). Quantitation of the SxlPe mRNAs by qRT-PCR supports the in situs – shown in Fig. S2B.