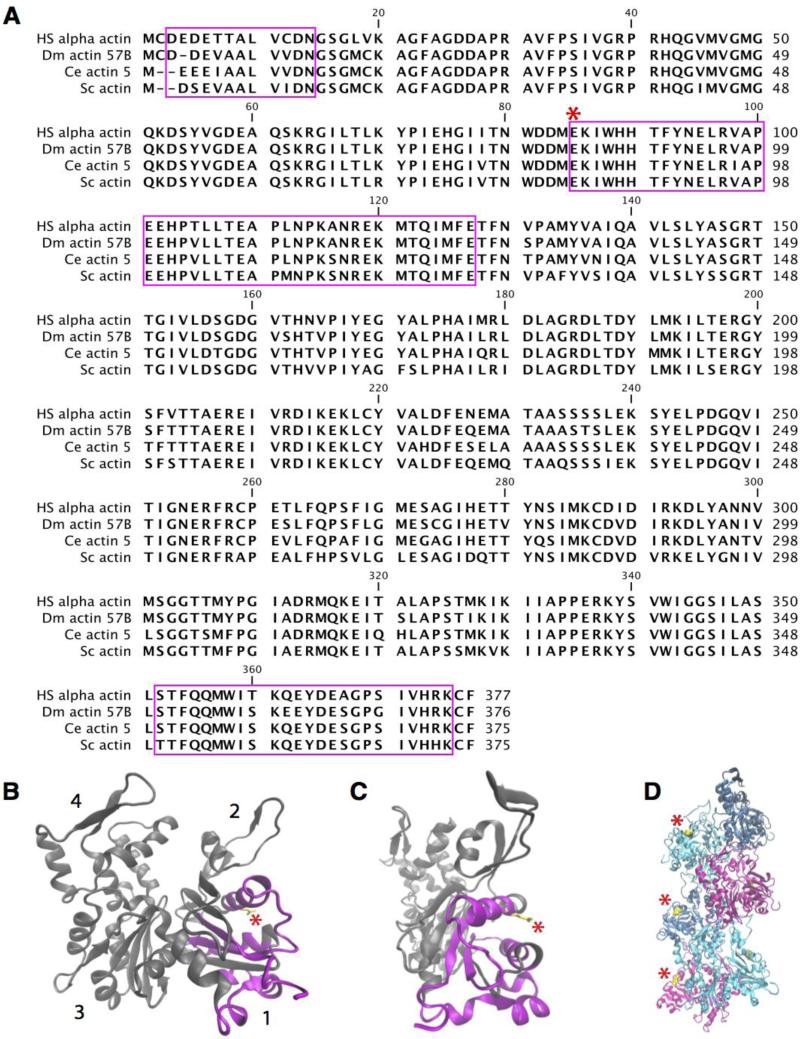
Fig. 3.
Glutamate 84 (E84) is a highly conserved residue and a part of the binding site for the CH domain superfamily. (A) Alignment of Drosophila (Dm) Actin 57B with homologs from Homo sapiens (Hs), Caenorhabditis elegans (Ce) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc). E84 (asterisk) is highly conserved from yeast to humans. Domains involved in binding members of the CH domain superfamily are indicated in magenta. (B-C) Crystal structure of the actin monomer is shown. The actin subdomains are denoted by numbers (1-4). E84 is highlighted in yellow and marked by an asterisk. The residues implicated in binding to members of the CH domain superfamily are highlighted in magenta. (D) Crystal structure of F-actin consisting of six differentially colored actin monomers. E84 localizes to the outside surface of the filament and is highlighted in yellow and marked by an asterisk.