Fig. 5.
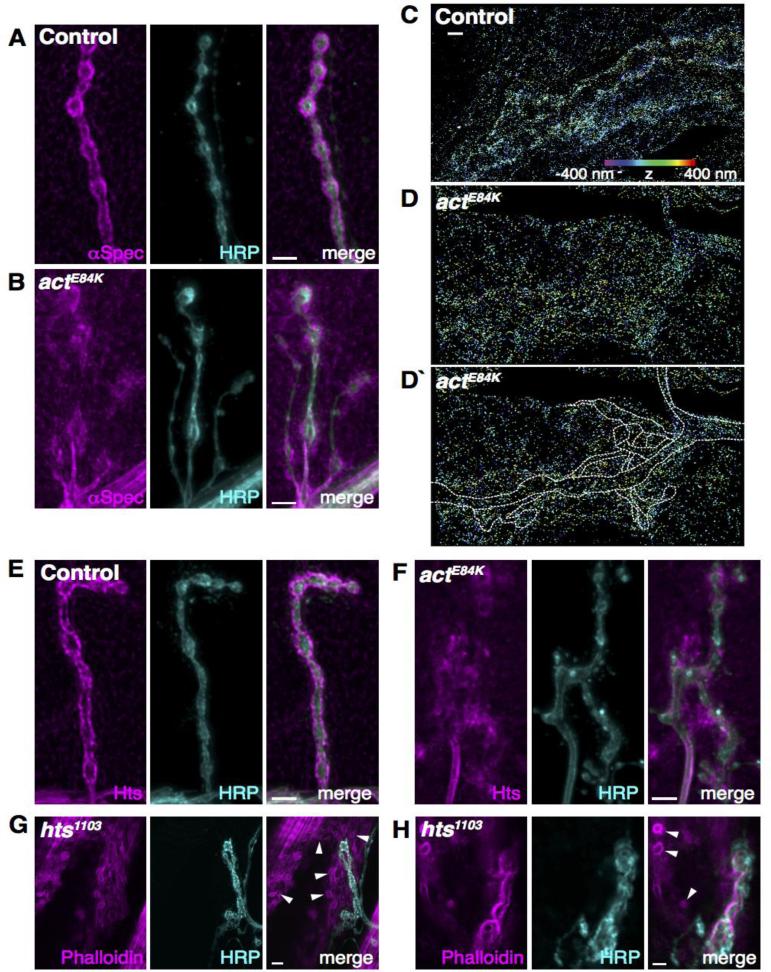
The postsynaptic spectrin network is disrupted in actE84K mutants. (A, B) The normal localization of α-spectrin surrounding control boutons (A) is disrupted in actE84K (B). Scale bar, 5μm. (C, D, D`) High-resolution three-dimensional STORM imaging reveals mislocalization of α-spectrin at the NMJ of actE84K animals. Spectrin is normally clustered tightly around presynaptic boutons in control animals (C), but is diffuse and disorganized in actE84K (D). An outline of the NMJ and axon (based on separate HRP staining) is shown for clarification (D`). Z positions in all STORM images are indicated by color, from −400 nm (violet) to 400 nm (red). Scale bar, 2 μm. (E, F) Adducin (Hts) is mislocalized in actE84K (F) compared to control (E). Scale bar, 5μm. (G, H) The postsynaptic actin cytoskeletal organization is disrupted in hts1103 mutants, with the formation of actin rings (subset marked by arrowheads) that are absent in cotnrols (compare to Fig. 4C). Scale bar, 5 μm in G and 2 μm in H.