Figure 3.
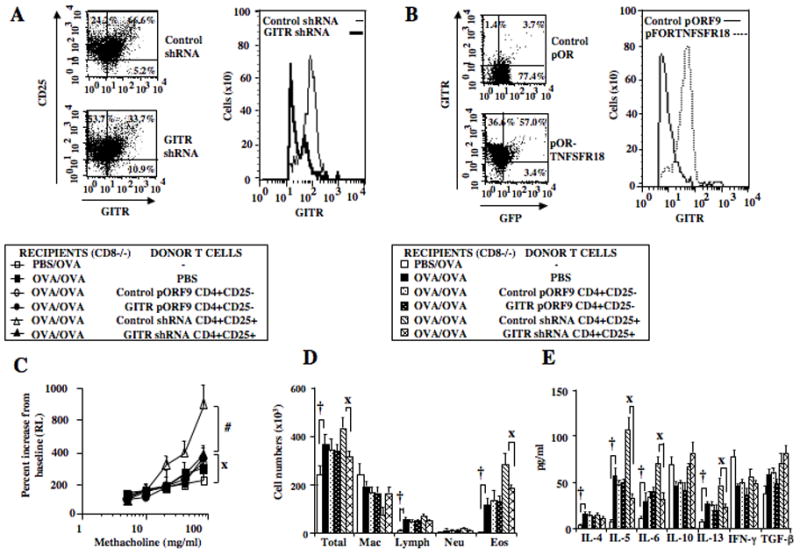
Effect of GITR silencing in CD4+CD25+ and GITR knock-in in CD4+CD25− T cells on enhancement of responses in sensitized and challenged CD8−/− recipients. Purified and activated CD4+CD25+ T cells were cotransfected with GFP/GITRshRNA or GFP/control shRNA lentivirus; CD4+CD25− T cells were nucleofected with GFP/mTNFRSF18 expression plasmids using Amaxa electroporation. GFP+ cells were sorted prior to adoptive transfer. A: FACS analysis of sorted GFP and GITR shRNA-coinfected CD4+CD25+ T cells, B: FACS analysis of sorted GFP and GITR expression vector (pORF9-mTNFSR18)-cotransfected CD4+CD25− T cells, C: AHR, D: BAL fluid inflammatory cell composition, E: BAL cytokine levels. Shown are the means±SEM from 3 independent experiments (4 mice/group, n=12). #p<0.05 comparing recipients given control shRNA to recipients given GITR shRNA transferred cells. Xp<0.05 comparing recipients of GITR shRNA transferred cells CD4+CD25+ T cells to mice challenged alone. †p<0.05 comparing sensitized and challenged mice to mice challenged alone. *p<0.05 comparing recipients given control pORF9-mcs transfected cells to recipients given pORF9-mTNFSR18 transferred cells.
