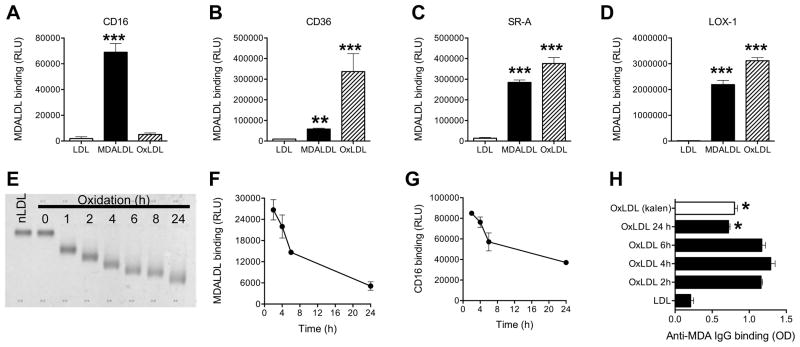
Figure 3. Mouse CD16 does not bind to oxLDL.
MDALDLbiotin or oxLDLbiotin (3 μg/ml) was added at sCD16 (A), sCD36 (B) or sSR-A (C) or sLOX-1 (D) coated plates. Binding was detected by luminescence assay. P, <0.001*** compared to nLDL binding. E, Electrophoretic mobility of differential oxidation of LDL. nLDLbiotin (200 μg/ml) was incubated with CuSO4 for indicated time and reaction was stopped by the addition of 0.1 mM EDTA. An aliquot (1 μg) was loaded on agarose gel and stained with Fat Red. nLDL (Kalen) and nLDLbiotin without the addition of copper (0 h) were used as controls. F, Decreased binding of differential oxLDLbiotin binding to sCD16 coated plates were determined by luminescence based assay using streptavidin-alkaline phosphatase. G, Decreased sCD16 binding to plate bound differential oxLDL. Differential oxLDL was prepared as described in 3F, using unlabeled nLDL. Differential oxLDL (5 μg/ml) was coated onto white ELISA plates for 16 h at 4°C. After blocking the plate with blocking buffer, sCD16 (3 μg/ml) was added sCD16 binding was detected using anti-poly His IgGbiotin followed by the addition of streptavidin-alkaline phosphatase in a luminescence assay. H, Loss of MDA epitopes in extensively oxLDL. Differential oxLDL (5 μg/ml) in PBS/1 mM EDTA was coated on ELISA plates. Affinity purified rabbit anti-MDA IgG binding was detected by ELISA using goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP and peroxidase substrate. OxLDL (copper oxidized LDL for 24 h) from a commercial source (Kalen) was used as an additional control. In all these assays values are mean ± SD of triplicate wells. Representation of 2–3 independent experiments is presented. P, <0.05* compared to 2 h oxLDL.