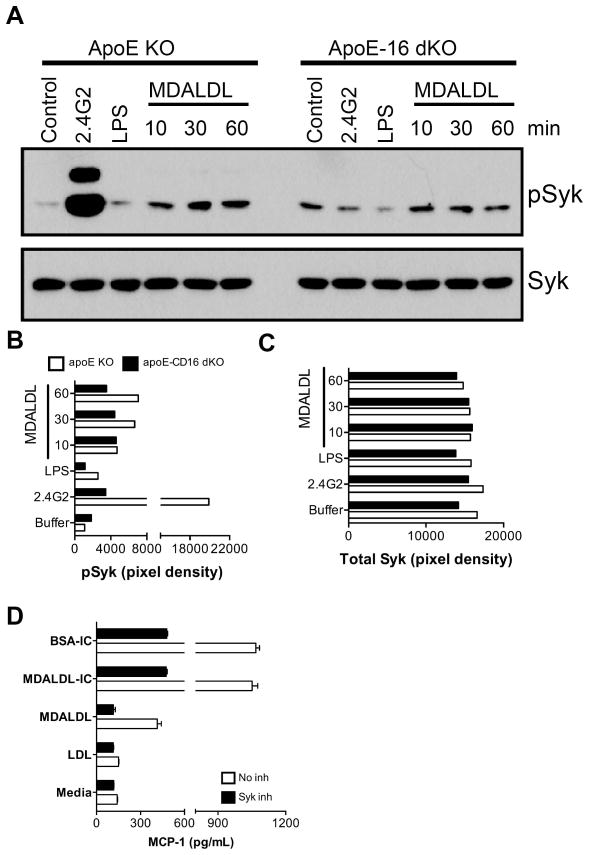
Figure 8. Decreased MDALDL-induced Syk activation in CD16 deficient macrophages.
A, Thioglycollate-elicited macrophages from apoE KO and apoE-CD16 DKO mice were plated and incubated with MDALDL (40 μg/ml) at indicated time. Macrophages incubated with anti-CD16 mAb (2.4G2, 5 μg/ml) followed by cross-linking with F(ab′)2-goat anti-rat IgG (10 μg/ml) was used as a positive control. LPS (100 ng/ml) treated cells were used as an additional control. Phospho-Syk (B) and total Syk (C) levels were determined by Western blot using specific antibodies and band intensities (pixel density) were determined in BioRad Quantity One software. C, Syk inhibitor blocked MDALDL-induced MCP-1 secretion. Macrophages were pre-incubated with Syk inhibitor III (5 μg/ml) for 30 min followed by the addition of MDALDL (40 μg/ml) or MDALDL-IC (20 μg/ml) for 18 h. Cells incubated with BSA-IC (15 μl/well) and nLDL (40 μg/ml) was used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Cells without the additional of Syk inhibitor or indicated reagents (media) was used to determine basal level of MCP-1 secretion. MCP-1 levels were determined by DuoSet ELISA kit from RND systems. Representation of two independent experiments is presented.