Figure 9. Identification of protein-nucleic acid interaction sites by crosslinking with tri-labeled oligonucleotide.
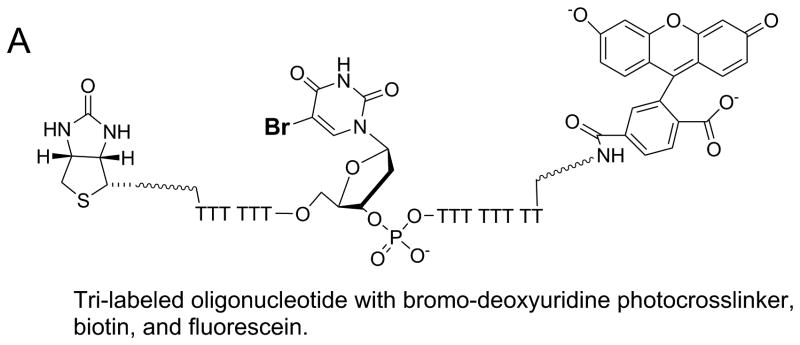
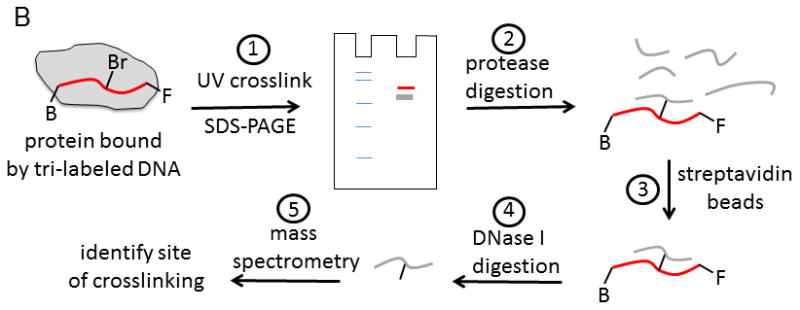
A. Oligonucleotide with three modifications for identification of protein-DNA interaction sites. A photoactivatable probe, bromo-deoxyuridine, can form covalent bonds with nearby amino acids upon exposure to the appropriate UV wavelength. The biotin label can be used to assist in isolation of the resulting DNA-protein crosslinks. The fluorescein label can aid in identification and isolation of peptide-DNA crosslinks for eventual characterization by mass spectrometry. B. Outline for steps involved in applying the tri-labeled oligonucleotide for the identification of DNA binding sites on proteins. Photocrosslinking of the DNA to the protein is followed by a series of steps to isolate the specific peptide that was involved in the crosslinking reaction. Mass spectrometry is used to identify the peptide. See text for more details of the protocol.
