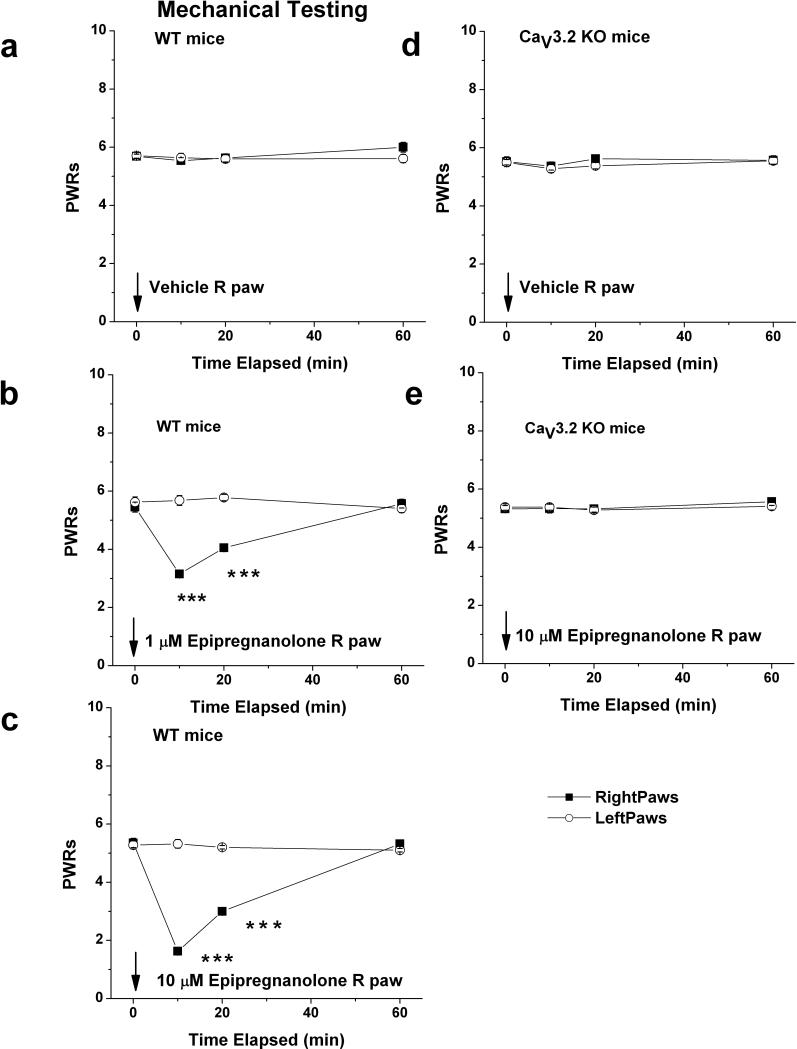
Figure 7. Local application of epipregnanolone induces potent dose-dependent analgesia to mechanical stimuli in WT mice but is ineffective in CaV3.2 KO mice.
a: Injection of 10 l of saline containing vehicle (0.1 % DMSO) into right paws (■) of WT (CaV3.2 +/+) mice had very little effects on mechanical PWRs. Note that PWRs in uninjected, left paws (○) also remained stable during the course of experiment. b,c: Dose dependent analgesia with 1 μM (b) and 10 μM (c) epipregnanolone is evidenced by significant prolongation of mechanical PWRs in injected (right paws) at 10 and 20 minutes following i.pl. injection. d,e: Injection of 10 μl of saline containing vehicle (d) or 10 μM epipregnanolone (e) into right paws (■) of KO (CaV3.2 −/−) mice had very little effects on mechanical PWRs.
Solid arrow indicates times of injection in all panels. Symbol *** indicates p < 0.001 for right versus left paw. We used 6-9 mice per experiment.