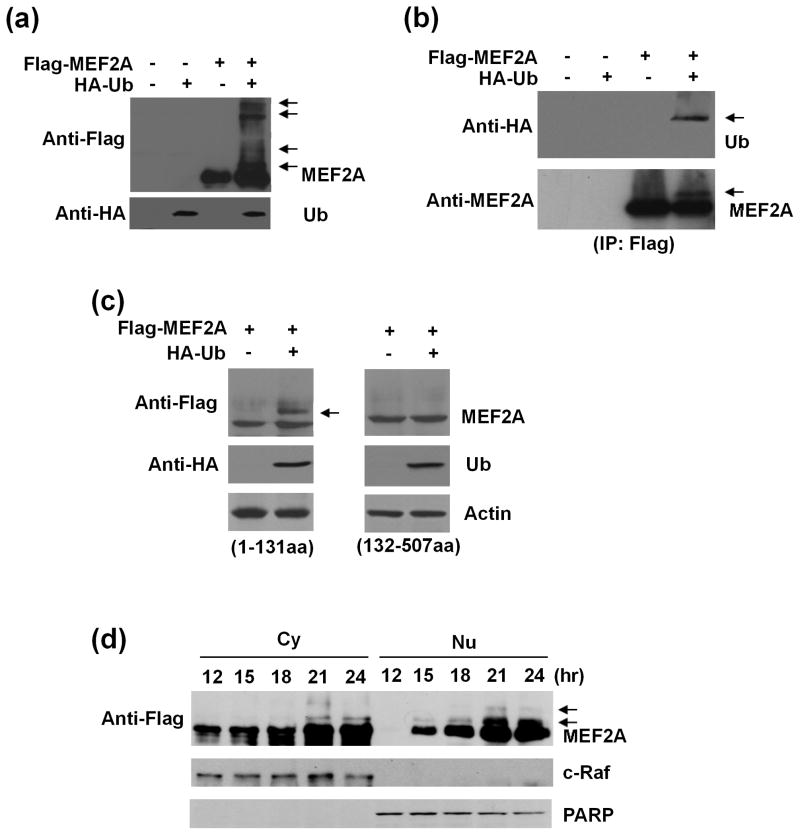
Fig. 1.
Ubiquitination of MEF2A in dopaminergic neuronal SN4741 cells. (a) SN4741 cells were transfected with Flag-MEF2A alone or together with HA-ubiquitin (HA-Ub) and analyzed by immunoblotting 24 hours later. Top panel: arrows indicated the higher molecular weight MEF2A. Bottom panel: blotting of HA-Ub. (b) After transfection as in (a), SN4741 cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using an anti-Flag antibody. The transferred membrane was immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-MEF2A antibodies sequentially. Arrows indicated the ubiquitinated MEF2A. (c) SN4741 cells were transfected with constructs for either Flag-MEF2A-N’-terminus (1-131aa) or Flag-MEF2A-C’-terminus (132-507aa) alone or with HA-Ub simultaneously. After 24 hours, cell lysates were analyzed by sequential immunoblotting with anti-Flag and anti-HA antibodies. Arrows indicated the ubiquitinated N’-terminal MEF2A. (d) SN4741 cells were transfected with Flag-MEF2A and HA-Ub simultaneously. Cytoplasmic (Cy) and nuclear (Nu) lysates prepared at indicated time points after transfection were analyzed using anti-Flag antibody. c-Raf was used as cytoplasmic marker and PARP as nuclear marker. Arrows indicated the ubiquitinated MEF2A.