Table 3.
Selective inhibition of NFκB mediated by resveratrol derivatives.
| Compounds tested | IC50 (μM)a | |
|---|---|---|
| 28b |
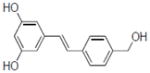
|
0.2±0.09 |
| 29 |
|
1.1±0.23 |
| 30b |
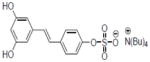
|
2.5±0.16 |
| 31b |
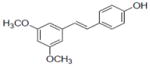
|
1.0±0.19 |
| 32 |
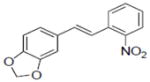
|
0.7±0.11 |
| 33b |
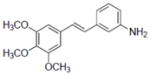
|
0.5±15 |
Sample concentration which caused 50% inhibition of TNF-induced NFκB activity treated with solvent (DMSO) only. N-Tosyl-L- phenylalanine-chloromethyl ketone (TPCK) and BAY-11 were used as a positive controls (IC50 = 3.8 and 2.0 μM, respectively).
Compounds 28, 30, 31, and 33 inhibited COX-1 with IC50 values of 0.87±0.04, 0.68±0.2, 2.8±0.67, and 2.0±0.57 μM, respectively. Compound 31 inhibited COX-2 with and IC50 value of 7.5±1.6 μM.
