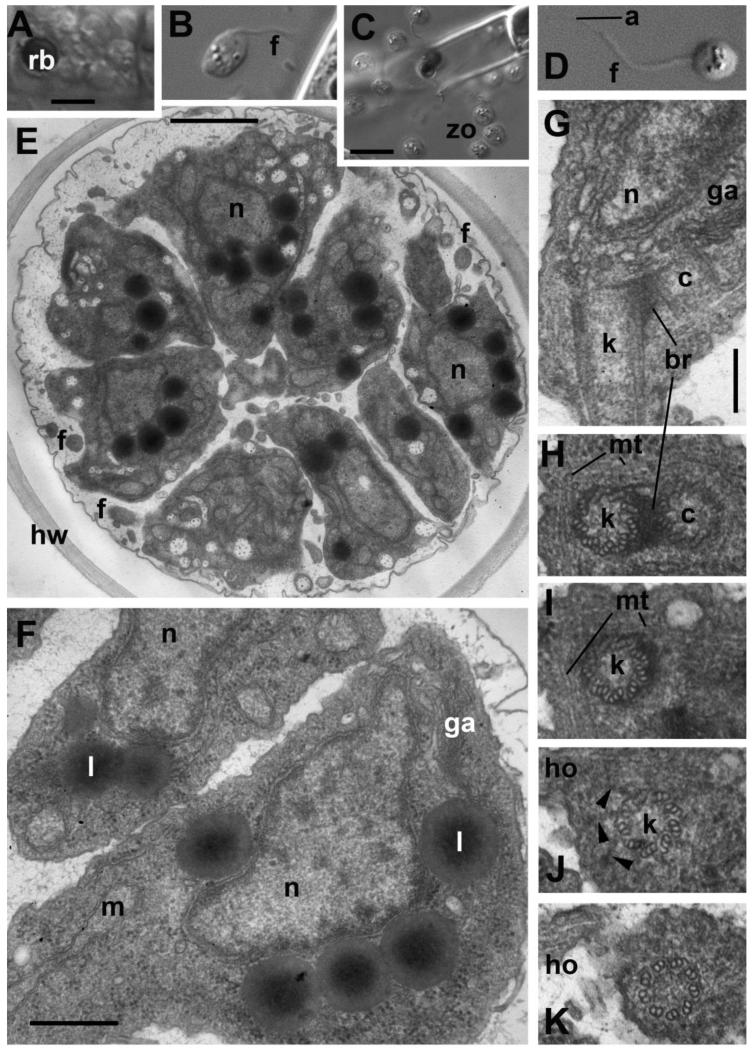
Figure 7. Zoospore structure and development in Aphelidium aff. melosirae seen by LM o living cells(A-D) and ultrathin sections observed by TEM (E-H).
A – recently divided plasmodium, B – amoeboid appearance of zoospore in algal vicinity, C – zoospore releasing, D – mature free-swimming zoospore. E-H – zoospore ultrastructure. E – general view of maturing zoospores inside the host cell wall, F – zoospore structure at higher magnification, G – kinetid at LS, H-K – series of kinetid consecutive thin sections from kinetosome and centriole (H) to flagellar transition zone (K). View from outside the cell. Arrowheads show the kinetosome transitional fibers. Abbreviations: a-acronema, br-bridge between kinetosome and centriole, c-centriole, f-flagellum, ga-Golgi apparatus, ho-horn, hw-host cell wall, k-kinetosome, l-lipid globule, m-mitochondrion, mi-microbody, mt-microtubules, n-nucleus, nu-nucleolus, rb-residual body, zo-zoospores. Scale bars: A, B, D - 5 μm, C – 10 μm, E – 1 μm, F – 500 nm, G-K – 200 nm.