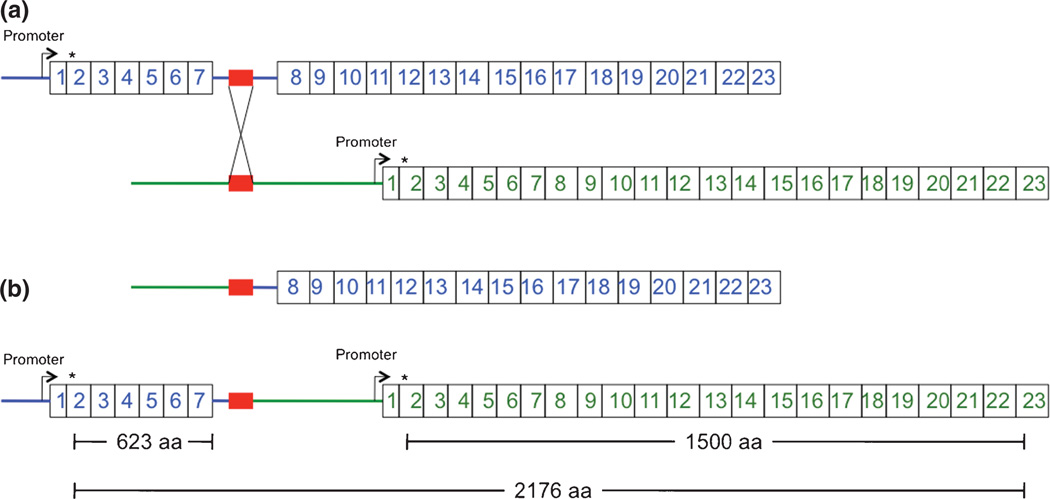
Fig. 1.
Proposed molecular mechanism resulting in tandem duplication of exons 1–7 of ATP7A. (a) Chromosomal misalignment of similar DNA sequences (red blocks) in intron 7 (enlarged) and the region upstream of ATP7A during meiosis results in an unequal crossing-over event. (b) The consequence of this event would be a deletion of ATP7A exons 1–7 on one X chromosome (top) and a tandem duplication on the other (bottom). The latter rearrangement, inherited by the male infant in this report, is predicted to generate three possible protein products, of which at least one (the 1500 amino acid normal length) should be functional. This interpretation assumes that the crossing-over event did not involve the ATP7A gene promoter. Asterisks denote the translation initiation site in ATP7A exon 2. aa, amino acids.