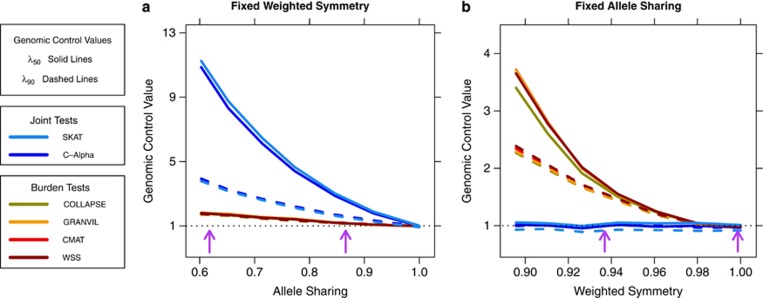
Figure 3.
The isolated effects of weighted symmetry and allele sharing on P-value inflation in gene-based rare variant tests. (a) For data set simulated with weighted symmetry fixed at WS=1 and decreasing allele sharing, inflation grows much larger for the joint tests than for the burden tests. (b) In contrast, for data sets simulated with allele sharing fixed at AS=1 and decreasing values of weighted symmetry, inflation in each burden test increases, whereas the joint tests remain well-controlled. Thus, the two classes of gene-based tests have differing responses to these patterns of rare variant population structure. The purple arrows in each plot indicate the minimum and maximum values of that statistic observed in the European JSFS. The range of empirical values explains why we observed higher levels of inflation in the joint tests.