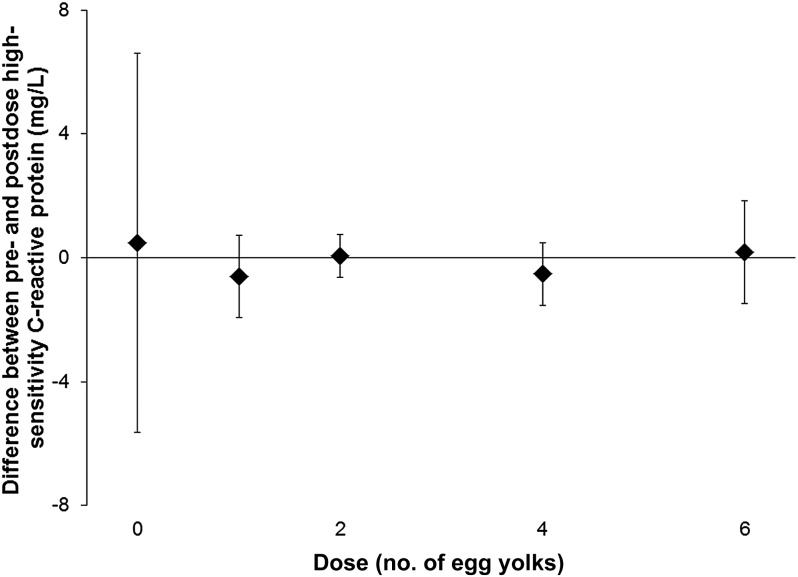
FIGURE 5.
Mean (±SD) differences (after dose minus before dose) in serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein concentrations. Six healthy volunteers (subjects) consumed a standardized low-choline diet on the day before each of 5 randomly assigned doses of 0, 1, 2, 4, or 6 egg yolks. Subjects consumed the egg dose for breakfast, followed by the same standardized low-choline lunch, dinner, and snacks as consumed the previous day. Each egg dose delivered 1.14 mmol (119 mg) total choline. Therefore, 0, 1, 2, 4, and 6 egg doses provided 0, 1.1, 2.3, 4.6, and 6.8 mmol (0, 119, 238, 476, and 712 mg) total choline, respectively, in addition to the standardized diet. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein was measured in serum collected immediately before and 24 h after each egg dose from each subject, and differences were calculated. According to paired t tests, there was no difference between predose and postdose values.