FIG 1.
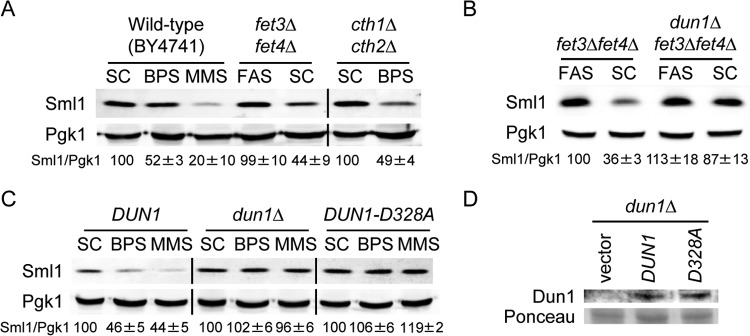
Dun1 kinase catalytic activity is required for the diminution of Sml1 protein levels upon genetic and nutritional iron depletion. (A) Sml1 protein abundance decreases in response to nutritional and genetic iron deficiencies. Wild-type BY4741, fet3Δ fet4Δ (SPY386), and cth1Δ cth2Δ (SPY122) yeast strains were grown at 30°C for 6 h in SC medium or SC medium with 100 μM BPS, SC medium with 300 μM FAS, or SC medium with 0.04% MMS added during the last 2 h. Sml1/Pgk1 protein values are shown as percentages of wild-type levels in SC medium (wild-type and fet3Δ fet4Δ strains) or cth1Δ cth2Δ in SC medium (cth1Δ cth2Δ strain). (B) DUN1 is required for Sml1 protein decrease in fet3Δ fet4Δ mutant cells. Yeast fet3Δ fet4Δ (SPY386) and dun1Δ fet3Δ fet4Δ (AXY1928) strains were grown as for panel A. Sml1/Pgk1 protein levels are relative to fet3Δ fet4Δ cells in FAS. (C) Dun1 kinase activity contributes to the drop in Sml1 protein caused by BPS treatment. Yeast dun1Δ (SPY350) cells transformed with plasmid pMH80 (DUN1), pRS416 (dun1Δ), or pMH62 (DUN1-D328A) were grown as for panel A. For each transformant, quantitation of Sml1/Pgk1 protein levels under BPS and MMS conditions are relative to the values obtained in SC medium. In all cases total proteins were extracted, and equal amounts were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Sml1 and Pgk1 protein levels were determined by immunoblotting with anti-Sml1 and anti-Pgk1 antibodies, respectively. Sml1/Pgk1 protein levels in panels A, B, and C were quantified, and the averages and standard deviations of at least three independent biological replicates are represented. (D) Dun1 and Dun1-D328A protein levels under low-iron conditions. Yeast dun1Δ (SPY350) cells transformed with plasmid pRS416, pMH80 (DUN1), or pMH62 (DUN1-D328A) were grown at 30°C for 6 h in SC medium with 100 μM BPS. Dun1 protein levels were determined by immunoblotting with an anti-Dun1 antibody, and Ponceau staining was used as a loading control.
