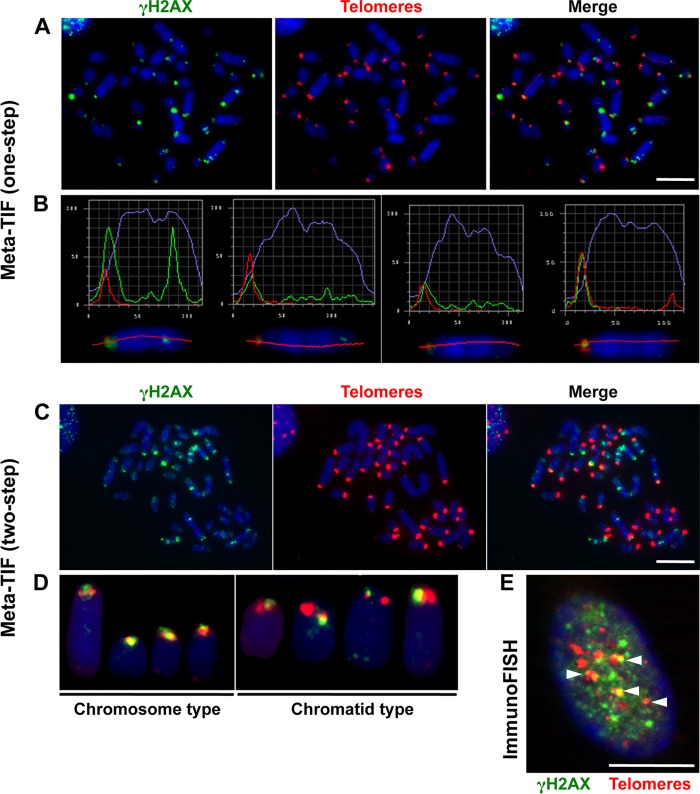
FIG 8.
Spontaneous telomere dysfunction in primary S. granarius fibroblasts. (A) Meta-TIF analysis of S. granarius fibroblasts (one-step protocol). Metaphase chromosomes were first stained with anti-γH2AX antibodies (green) and subsequently stained with a telomeric PNA probe (red) for detection of telomere-induced foci (TIF). Chromosomes were counterstained with DAPI (blue). (B) Relative green and red fluorescence intensities of particular chromosomes from the metaphase spread shown in panel A, illustrating either perfect colocalization of red and green signals or the spread of green signals toward the interstitial region. (C) Meta-TIF analysis of S. granarius fibroblasts by a two-step protocol involving immunofluorescence assay with anti-γH2AX antibodies, with image acquisition (green; left panel), as well as hybridization with a telomeric PNA probe, with visualization (red; middle panel). The right panel show the merge of the two visualization steps. (D) Illustration of chromosome- and chromatid-type TIF detected in a two-step experiment. The images show staining with anti-γH2AX antibodies (green) and a telomeric PNA probe (red). A quantification of these experiments is presented in Table 3. (E) Detection of TIF in S. granarius interphase nucleus by a one-step protocol. The image shows staining with anti-γH2AX antibodies (green) and a telomeric PNA probe (red). Bars, 10 μm.