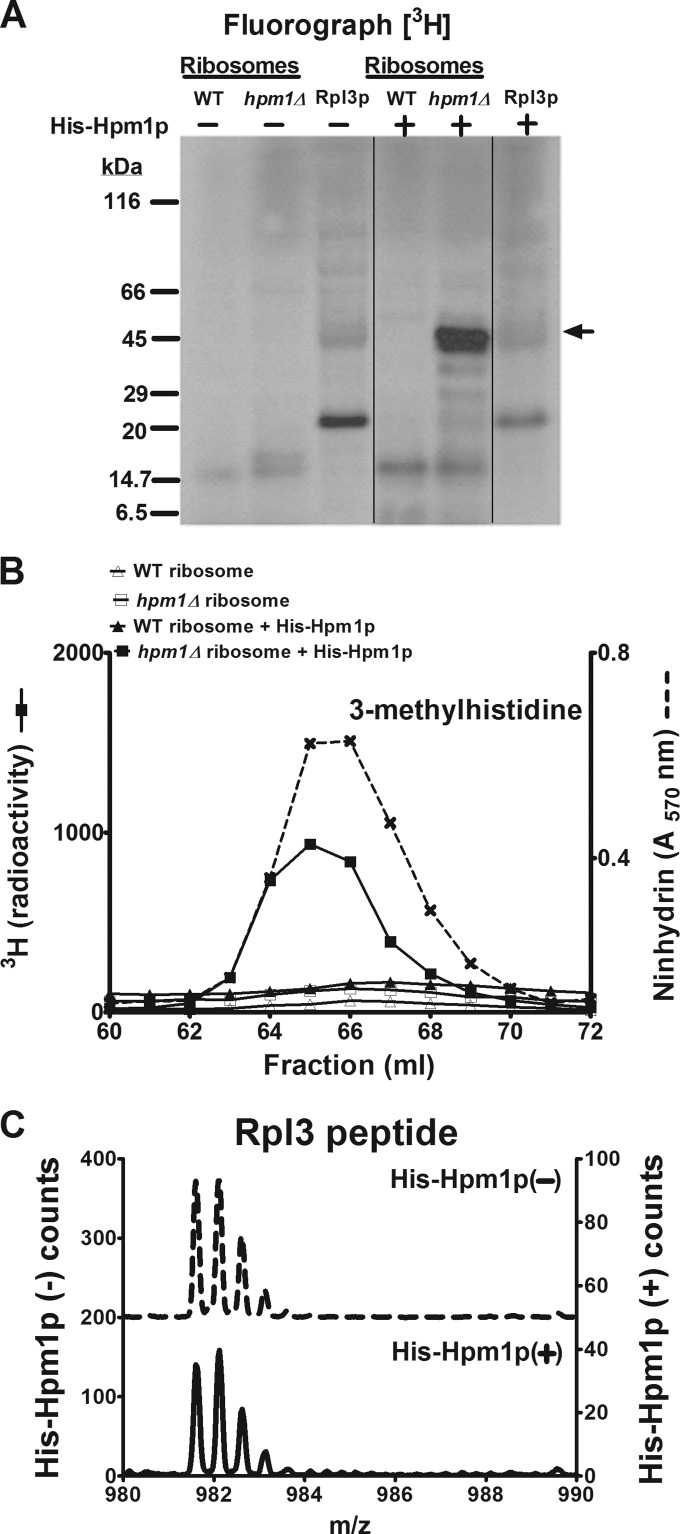
FIG 2.
Hpm1p can methylate Rpl3p on intact ribosomes but not free Rpl3p. (A) A 46-μg sample of crude ribosome protein isolated as described in Materials and Methods from WT and hpm1Δ mutant cells or 46 μg of recombinant Rpl3p was incubated with or without recombinant, histidine-tagged Hpm1p (His-Hpm1p; 12 μg) in the presence of 1 μM [3H]AdoMet and 100 mM sodium chloride–100 mM sodium phosphate (pH 7.5) (methylation buffer) for 5 h at 30°C. Reactions were terminated by the addition of equal volume of 2× Laemmli sample buffer, and proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and fluorography as described in Materials and Methods. Film was incubated with the dried gel for 7 weeks at −80°C. The arrow indicates the approximate position of recombinant His-Rpl3p. The radiolabeled band at about 20 kDa appears to reflect a bacterial contaminant in the His-Rpl3p preparation. Vertical lines show where nonrelevant lanes were removed from the single gel. (B) Thirty-seven-microgram samples of crude ribosome protein from WT and hpm1Δ mutant cells were incubated with or without His-Hpm1p as described above. Proteins were trichloroacetic acid precipitated and acid hydrolyzed for amino acid analysis as described in Materials and Methods, except that fractions eluting at 60 to 72 ml were collected and the 3H radioactivity of 900 μl of each fraction was counted (reported in counts per minute). Ninhydrin, absorbance of the 3-methylhistidine standard. (C) The synthetic peptide WGTKKLPRKTHRGLRK (Biosynthesis, Lewisville, TX), corresponding to the methylated region of Rpl3p, was incubated with or without His-Hpm1p (30 μg) in the presence of 200 μM S-adenosyl-l-methionine p-toluenesulfonate (Sigma) and methylation buffer for 16 h at 30°C. Reactions were terminated with trifluoroacetic acid to a final concentration of 1%, and the products were fractionated by high-performance liquid chromatography with a PLRP-S reverse-phase column (pore size, 300 Å; bead size, 5 μm; 120 by 2 mm; Polymer Laboratories, Amherst, MA). The column was maintained at 50°C and initially equilibrated in 95% solvent A (0.1% trifluoroacetic acid in water) and 5% solvent B (0.1% trifluoroacetic acid in acetonitrile) at a flow rate of 0.5 ml/min. The following program was used: 10 min of 5% B, 25 min of a gradient to 60% B, 1 min of a gradient to 100% B, 5 min of 100% B, 1 min of a gradient to 5% B, and 8 min of 5% B. The column effluent was directed to the electrospray ion source of a QSTAR Elite (Applied Biosystems) mass spectrometer running in MS-only mode and was calibrated with external peptide standards. The left y axis represents the counts in the absence of His-Hpm1p, and the right y axis represents the counts in the presence of His-Hpm1p.