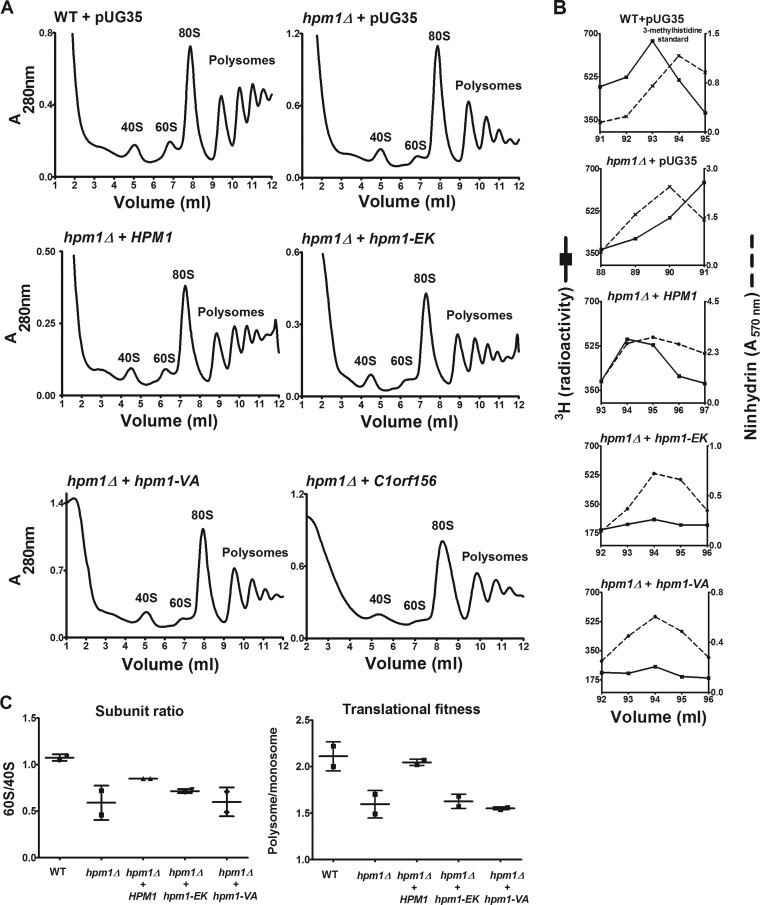
FIG 5.
Plasmids containing WT HPM1 but not the human homolog C1orf156 can rescue hpm1Δ mutant defects in large-subunit biogenesis and translational initiation. (A) hpm1Δ mutant cells were transformed with the pUG35 plasmid containing the HPM1 gene, its human homolog C1orf156, or HPM1 active-site mutants under the control of the Met25 promoter. As controls, WT and hpm1Δ mutant cells were transformed with empty pUG35 expressing only GFP. The hpm1(EK) and hpm1(VA) genes have mutations in motif 1 of the MT domain, which is involved in AdoMet binding, i.e., EIGCG to KIVCE (EK) and VEIG to AAAA (VA). Cells were grown overnight in SD-Ura-Met at 30°C in a rotary shaker. Cells were then diluted in 100 ml of fresh SD-Ura-Met to an OD600 of 0.01 and grown overnight at 30°C until they reached an OD600 of 0.8 to 1.0. Polysome profile analysis was done as described in Materials and Methods. The HPM1, C1orf156, hpm1(EK), and hpm1(VA) genes were cloned into pUG35 with their stop codons to express the genes without the GFP tag. (B) WT and hpm1Δ mutant cells containing the plasmids described in panel A were labeled in vivo with [3H]AdoMet as described in Materials and Methods, except that 3.5 OD600 units of cells was labeled for 1 h. Total lysates were prepared in buffer C and acid hydrolyzed for amino acid analysis as described in Materials and Methods, except that the column was kept at 35°C and that 900 μl of each fraction was taken for radioactivity determination. 3H radioactivity is shown in counts per minute, and ninhydrin absorbance of the 3-methylhistidine standard was measured. (C) Quantification of polysome profiles. Ratios were calculated by determining the areas of the 40S, 60S, monosome (80S), and polysome peaks with Graphical Analysis 3.8.4 software. Error bars represent standard deviations of two independent experiments. The subunit ratio and translational fitness differences were not statistically significant at the P < 0.05 level.