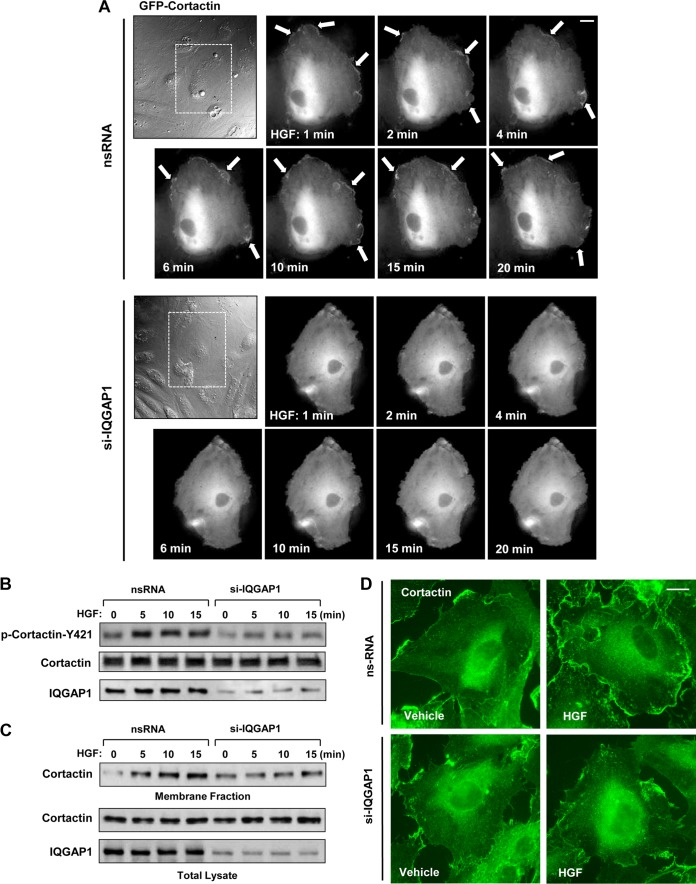
FIG 2.
IQGAP1 mediates HGF-induced cortactin activation. HPAEC transfected with IQGAP1-specific siRNA (si-IQGAP1) or nonspecific RNA (nsRNA) (100 nM, 72 h) were stimulated with HGF (50 ng/ml). (A) Live-cell imaging of control and IQGAP1-depleted cells expressing GFP-cortactin. Snapshots depict HGF-induced cortical dynamics at the periphery of control and IQGAP1-depleted cells. Arrows indicate cortactin accumulation at cell edges. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Bar = 5 μm. (B) HGF-induced cortactin phosphorylation in control and IQGAP1-depleted EC was evaluated by Western blotting with phospho-Y421-cortactin antibody. Equal protein loading was confirmed by probing the membrane with a cortactin antibody. siRNA-induced IQGAP1 knockdown was confirmed by probing whole-cell lysates with an IQGAP1 antibody. (C) Cells transfected with nonspecific RNA or IQGAP1-specific siRNA were treated with HGF for 5, 10, or 15 min, and membrane translocation of cortactin was analyzed by Western blot analysis of EC membrane fractions. siRNA-induced IQGAP1 knockdown was confirmed by probing whole-cell lysates with IQGAP1 antibody. Results are representative of four independent experiments. (D) Control and IQGAP1-depleted pulmonary EC cultures were stimulated with HGF (50 ng/ml, 10 min). HGF-induced cortactin translocation was evaluated by immunofluorescence staining of formaldehyde-fixed EC. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Bar = 5 μm.