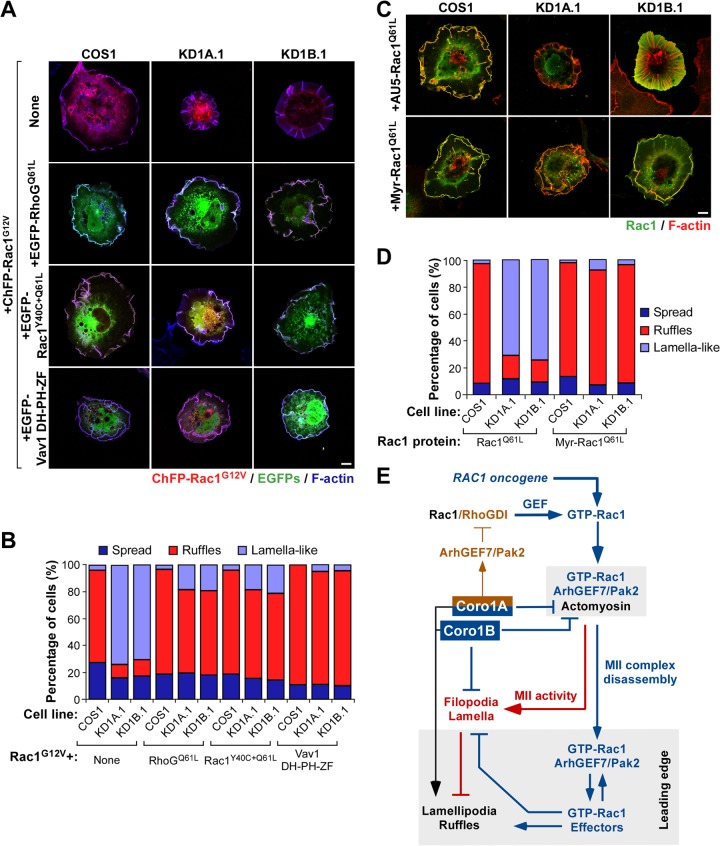
FIG 11.
Subcellular relocalization of Rac1 rescues membrane ruffling in Coro1-depleted cells. (A to D) Representative images (A and C) and quantification (n = 3; 150 cells/transfection) (B and D) of the cytoskeletal changes induced by the indicated combinations of GTPases (A to D) and the catalytic DH-PH-ZF region of the Vav1 Rho GEF (A and B) in parental and CORO1A and CORO1B knockdown cells. In panel A, colocalization of the indicated Rho and Vav1 proteins with both ChFP-Rac1G12V and F-actin is shown in white. In panel C, colocalization of the Rac1 proteins and F-actin is shown in yellow. Scale bars, 10 μm. (E) Integrated view of the results reported. The Coro1-dependent route described is indicated by blue (functional steps) and red (dysfunctional steps induced upon Coro1 depletion) lines. The previously described Coro1A-dependent loop involved in optimal Rac1 activation is shown with brown lines. The intrinsic role of Coro1 in F-actin regulation is shown in black. Activation and inactivation steps are indicated by arrows and blunted lines, respectively. MII-rich and leading-edge areas are shaded.