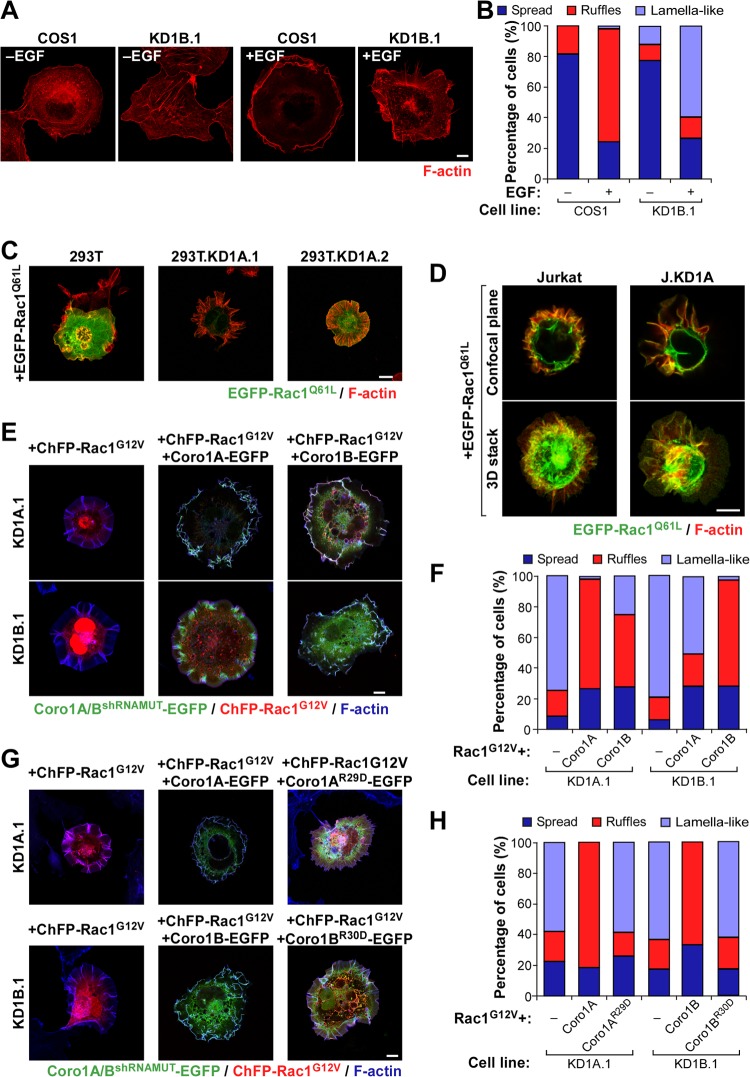
FIG 4.
Cell-type-independent and nonredundant implication of Coro1 proteins in Rac1 cytoskeletal signaling. (A and B) Representative images (A) and quantification (n = 3; 150 cells/condition) (B) of F-actin organization induced by EGF in the indicated cell lines. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C and D) Examples of the cytoskeletal changes induced by ectopic EGFP-Rac1Q61L in the indicated HEK 293T (C) and Jurkat (D) cells. In the case of Jurkat cells, a confocal plane and a Z-stack 3-dimensional (3D) reconstruction are shown. 293T.KD1A.1 and 293T.KD1A.2 are two independent pools of CORO1A knockdown HEK 293T cells. J.KD1A is a pool of CORO1A knockdown Jurkat cells. Colocalization areas of Rac1 with F-actin are shown in yellow. Scale bars, 10 (C) and 5 (D) μm. (E to H) Representative images (E and G) and quantification (n = 3; 150 cells/condition) (F and H) of the cytoskeletal phenotype exhibited by Coro1-depleted COS1 cells (E and G, left) upon ectopic expression of the indicated combinations of ChFP-Rac1G12V and Coro1-EGFP proteins. Coro1A/BshRNAMUT-EGFP refers to the ectopic protein that cannot be targeted by the shRNA harbored in knockdown cells. In panels E and G, colocalization areas of Rac1 with Coro1 proteins and F-actin are shown in white. Scale bars, 10 μm.