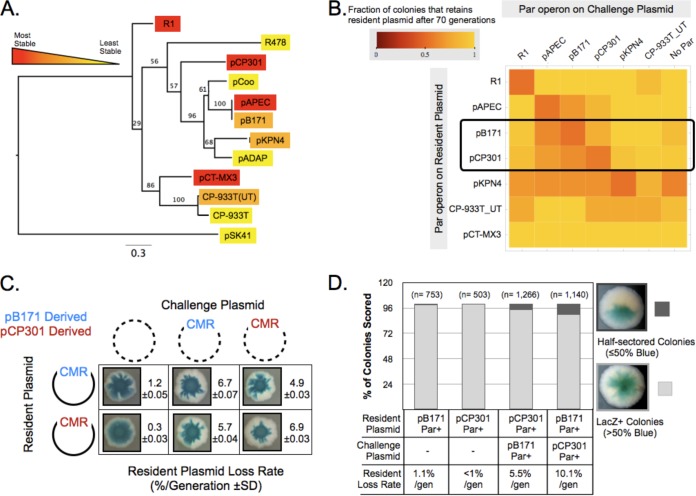
FIG 2.
Limited plasmid partition incompatibility detected between type II partitioning homologs. (A) A maximum-likelihood-based phylogenetic tree of the ParM amino acid sequence of the type II partitioning operons utilized in this study, indicating the stability of resident plasmids containing them. Bootstrap values are shown. (B) A matrix displaying the results of quantitative compatibility assays for the indicated combinations of partitioning operons. Increasingly red squares indicate the levels of partition incompatibility observed. (C) Qualitative and quantitative incompatibility assay results showing the mutual incompatibility between ParpB171 and ParpCP301 plasmids. CMR, chloramphenicol resistance plasmid. (D) Direct detection of resident plasmid loss in the first cell division of a colony by the formation of half-sectored colonies for β-galactosidase expression. The plasmid pairs tested are indicated.