FIG 5.
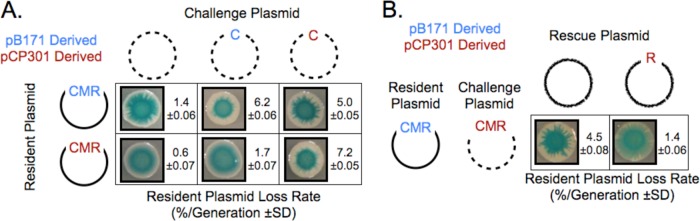
Partition incompatibility depends on competition between ParRpB171 and ParRpCP301 for binding to parCpCP301. (A) Binding of ParRpB171 to parCpCP301 causes segregation incompatibility. Data represent the results of a quantitative and qualitative plasmid compatibility assay comparing a challenge plasmid carrying parCpB171 to a challenge plasmid carrying parCpCP301 with respect to the stability of ParpB171 or ParpCP301 resident plasmids. (B) Overexpression of ParRpCP301 protects a ParpB171 resident plasmid from incompatibility. Data represent the results of quantitative and qualitative plasmid compatibility assays showing the incompatibility between a resident ParpB171 plasmid and a challenge ParpCP301 plasmid under conditions of constitutive expression of either GFP (Par− plasmid) or ParRpCP301 from a third plasmid.
